Given below are a list of projects I have worked on. Please feel free to get in touch, should you wish to learn more about any of them. I have attached the code to all of them, wherever relevant.
Evaluation of Visual SLAM Techniques
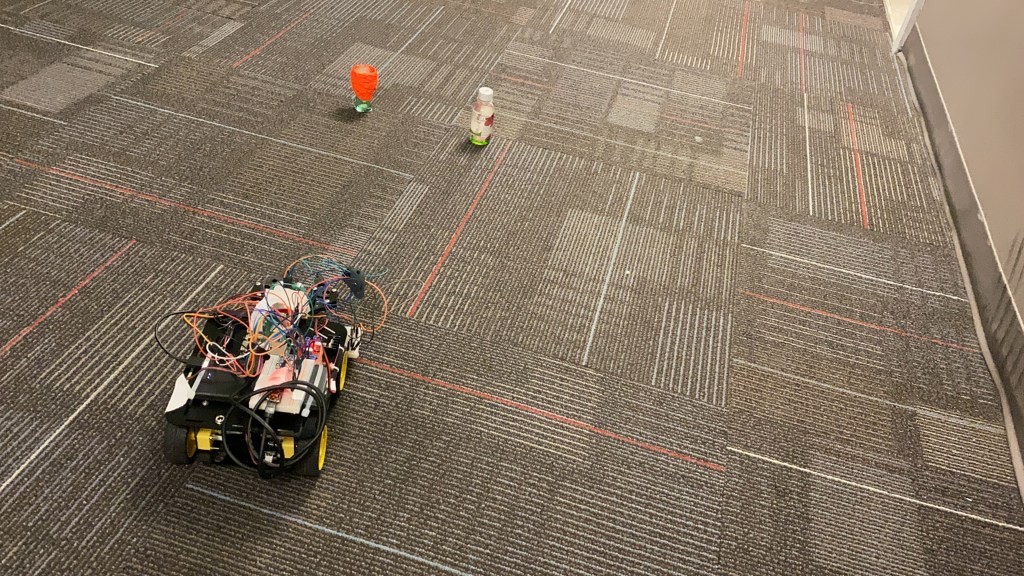
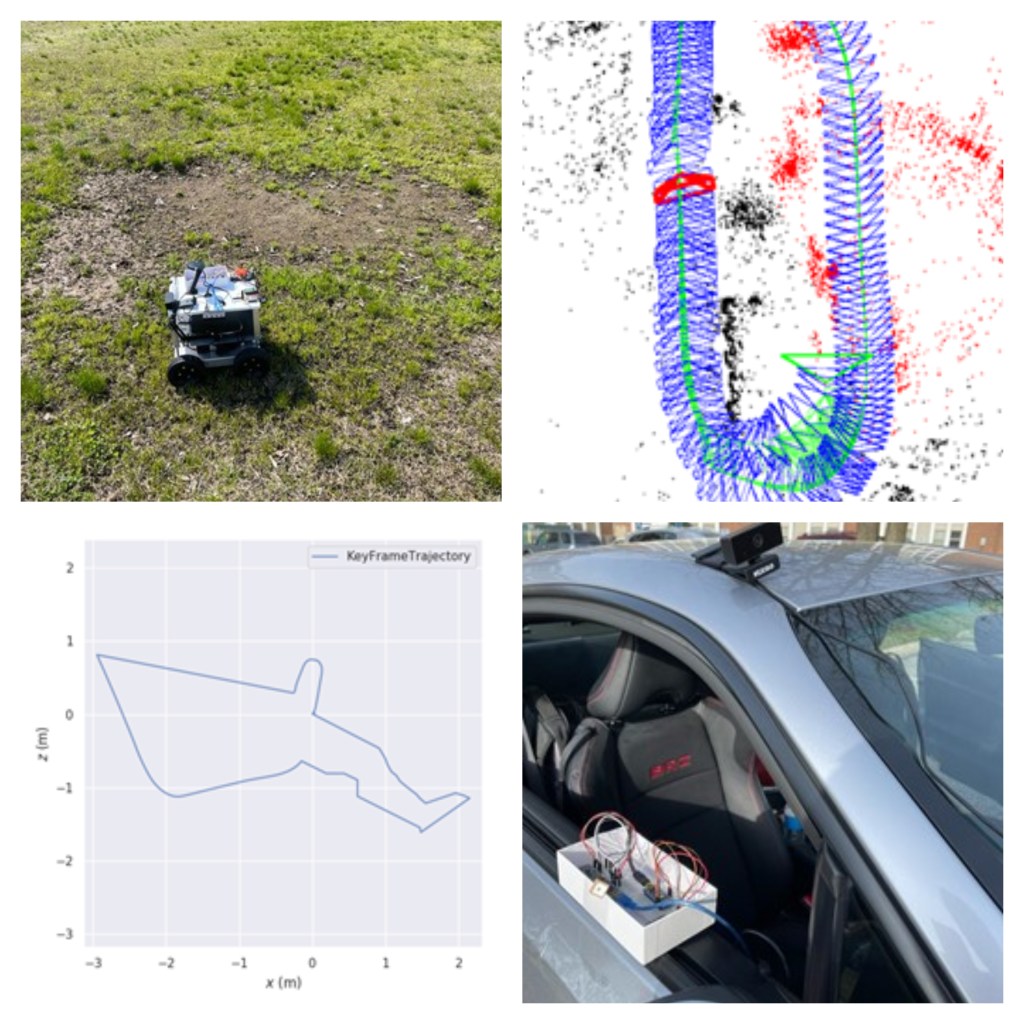
This study explores Visual SLAM, its applications and works towards developing a system that has applications in navigating a mobile robot in an urban environment/agricultural field.
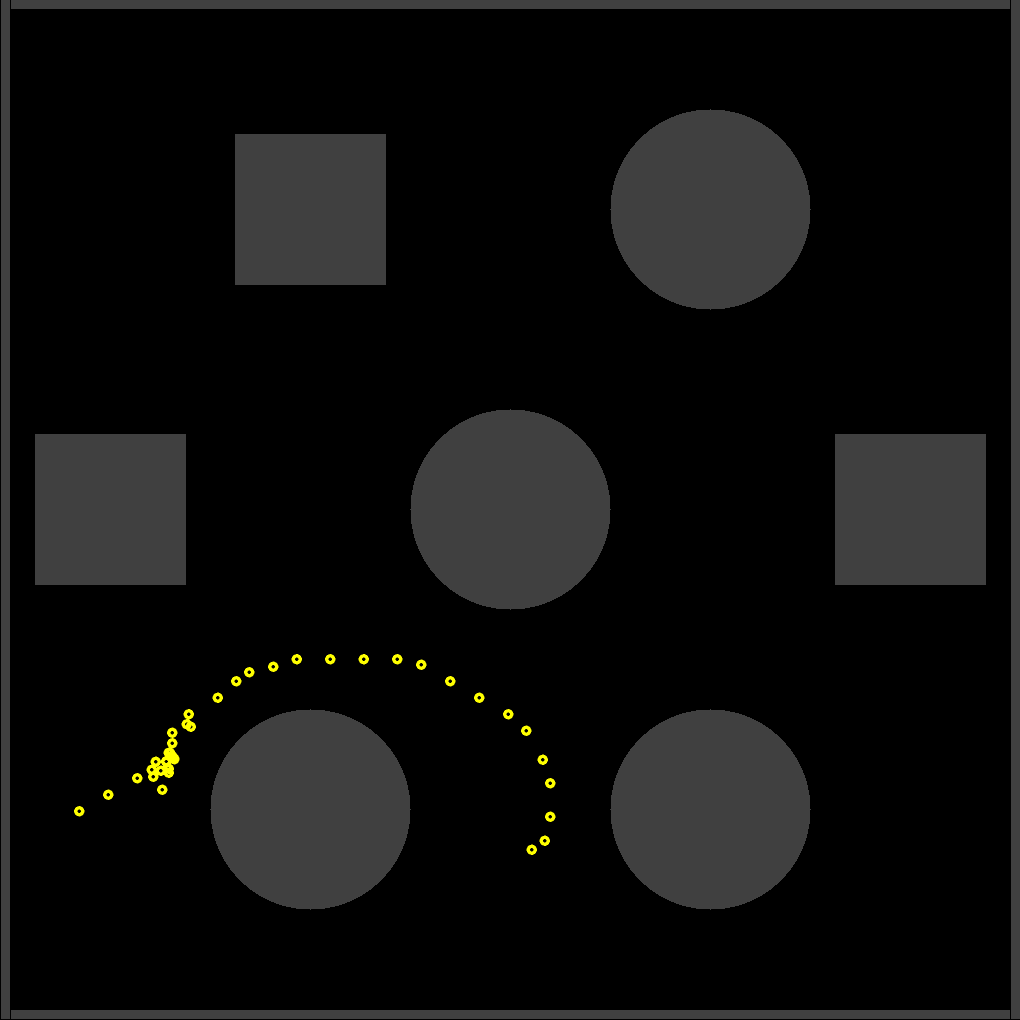
The mobile robot relies on Visual SLAM for autonomous navigation. The data collected is verified with the data collected from an Inertial Measurement Units (IMU) and a Global Position System (GPS).
The experiments were conducted on urban environments and agricultural settings to map out the path driven by the robot and the plot drawn was verified by plotting the data through GPS. For this study, I decided to limit the scope to ORB-SLAM2, ORB-SLAM3 and OpenVSLAM.

The tests on a custom dataset indicated that Visual SLAM does not perform very well in a field, as opposed to a smoother environment for the mobile robot/vehicle to drive on.

Additionally, there is a significant performance difference between ORB-SLAM2 and ORB-SLAM3 when features are lost, and the map fails to initialize. A few suggestions and future scope are also mentioned towards the end of the report.
Please find the entire report, link to all datasets, and important repositories here:
Please find all the GitHub Links here:

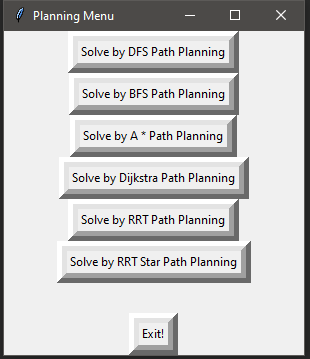
Planning Algorithm – Tkinter UI Platform
This is a long-term project I am working on at the moment. It is a user Interface based python program that helps you visualize various planning algorithms.
The Menu looks like the image attached below:
Once you click on the search algorithm of your choice, click on a start and a goal point.
The algorithm will now solve itself. The output will look like follows:
View a solving video here:
The code is still in works. I will post the GitHub repository here shortly.
2 Player Scored Ice Hockey – OpenCV and Python
The program runs a 2 player ice hockey that hits the ball to each other.
The game resets every time a player scores a point. The scores are also recorded on the screen.
View the full GitHub code here:

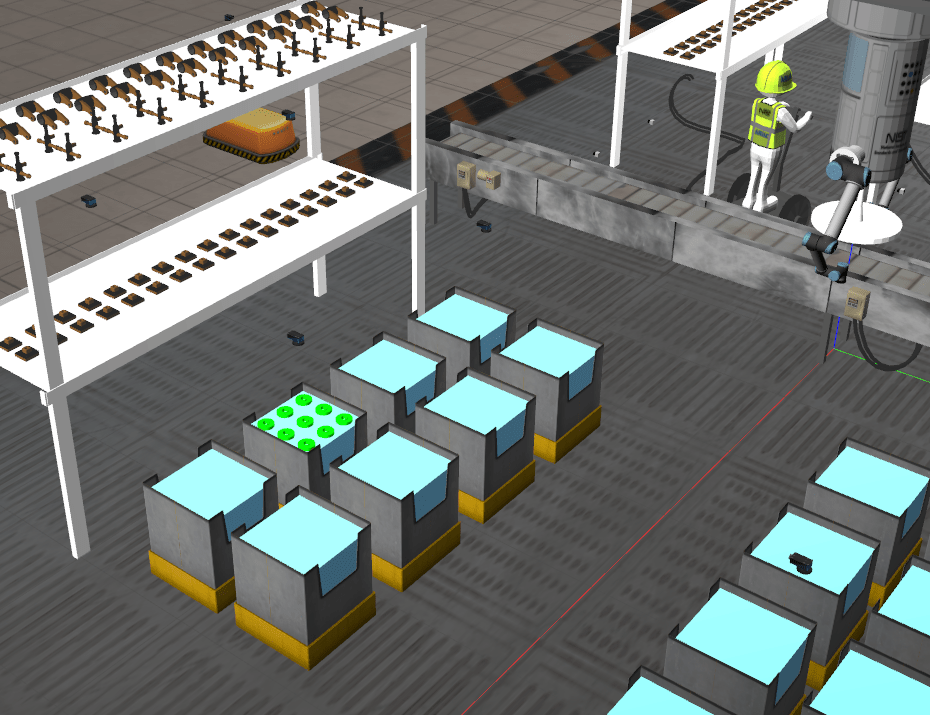
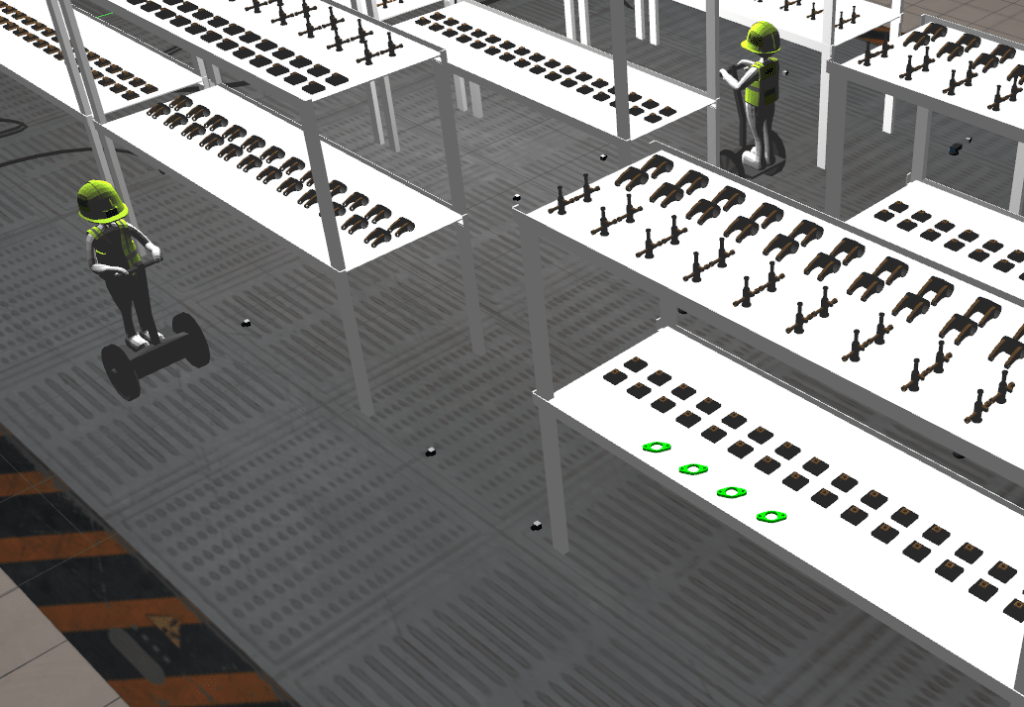
ARIAC NIST Competition
This was 6 month-long project that involved simulating a manufacturing scenario with real-life problems.
All the packages and complete workspace can be found here:
The simulation involved finding and collecting parts, planning the path as per the obstacles, and completing orders. The robot tasked to do this was a 6 d-o-f gantry robot.
The programme was tasked with finding the parts placed in shelves and bins as shown below.
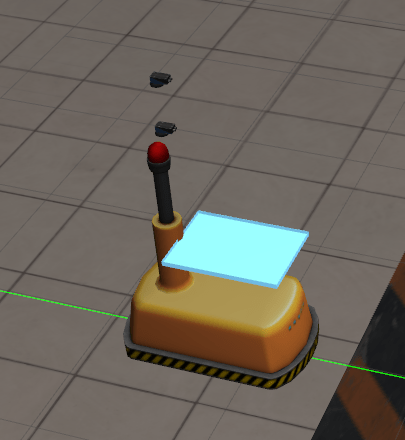
Parts would also be found on the conveyor belt, shown below.
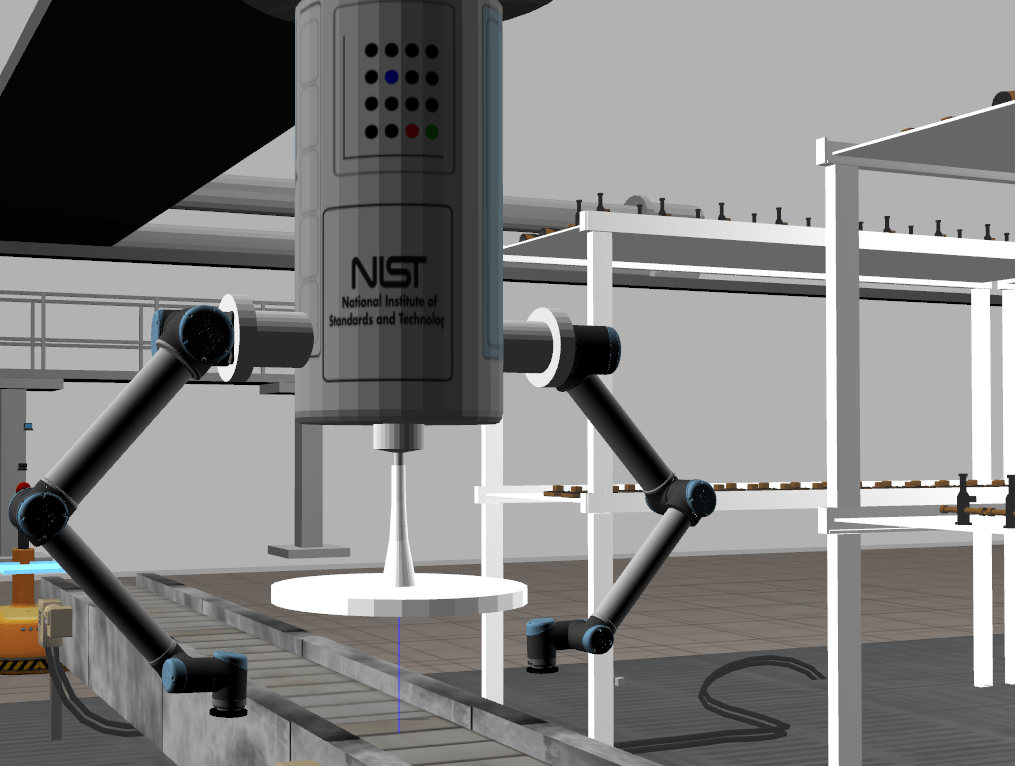
The robot had to retrieve these parts and deliver them to the AGV.
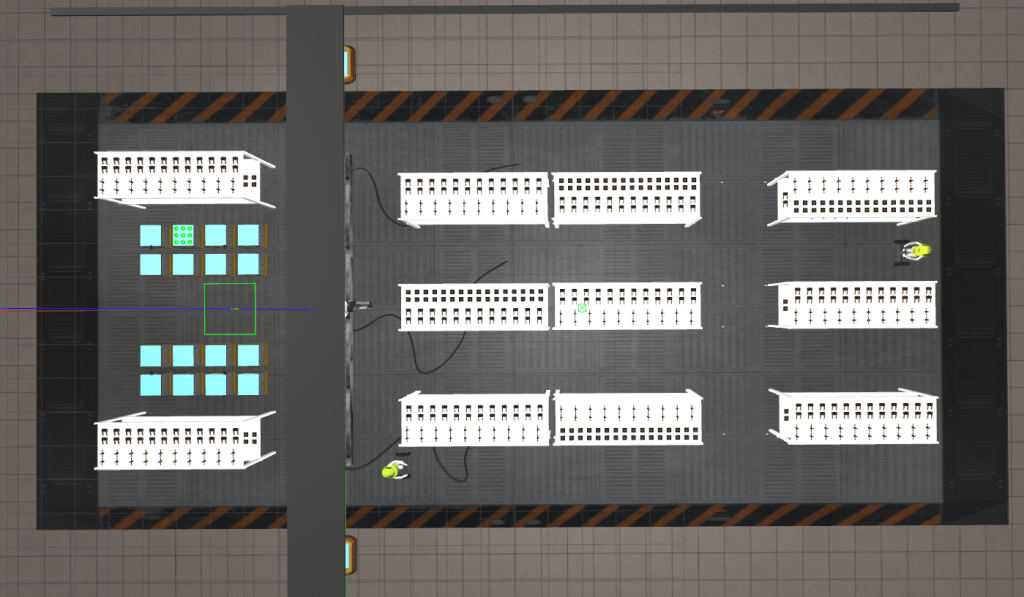
The environment involved inspectors and shelves with varying gaps. A birds-eye view of the factory can be seen below.
The final code base can be found in my GitHub linked below.
Click here to see my entire work-log.
The project was an exercise in ROS and C++ and has been one of the best team-project I have ever worked on.
Other relevant links can be found here:
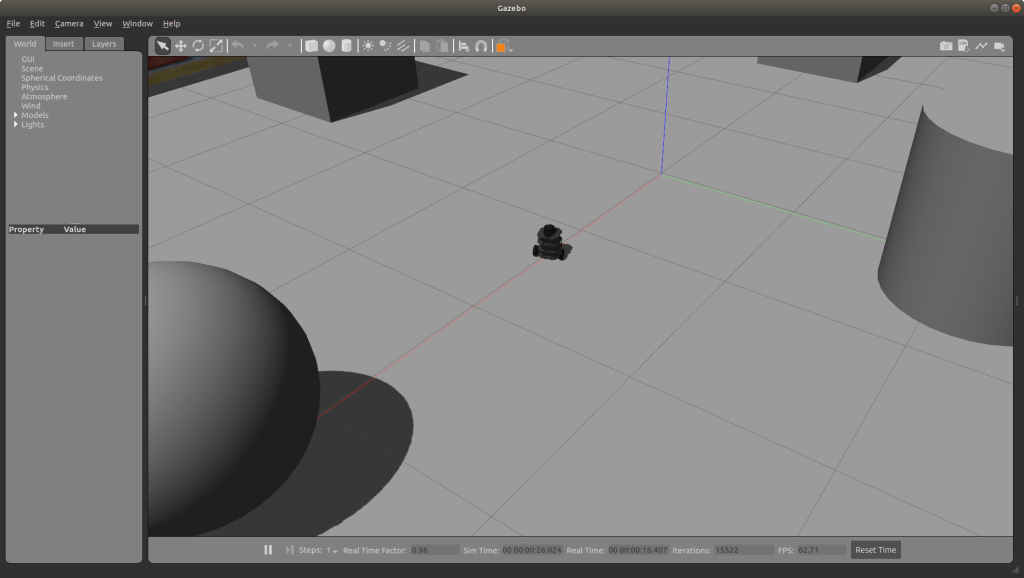
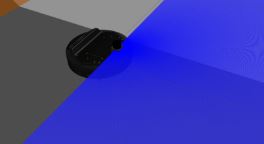
iRobot Roomba like Turtlebot
This project simulated a turtlebot3 waffle to behave like a Roomba vacuum cleaner.
The robot goes around within a confined space and detects any obstacles through its LIDAR and turns and avoids it.
This programme was developed in C++ and simulated using ROS and Gazebo. A visualization of the same can be seen below.
All the code has been documented and formatted using cppcheck, cpplint, and Google formatted. You can view it all on my GitHub repository linked below.
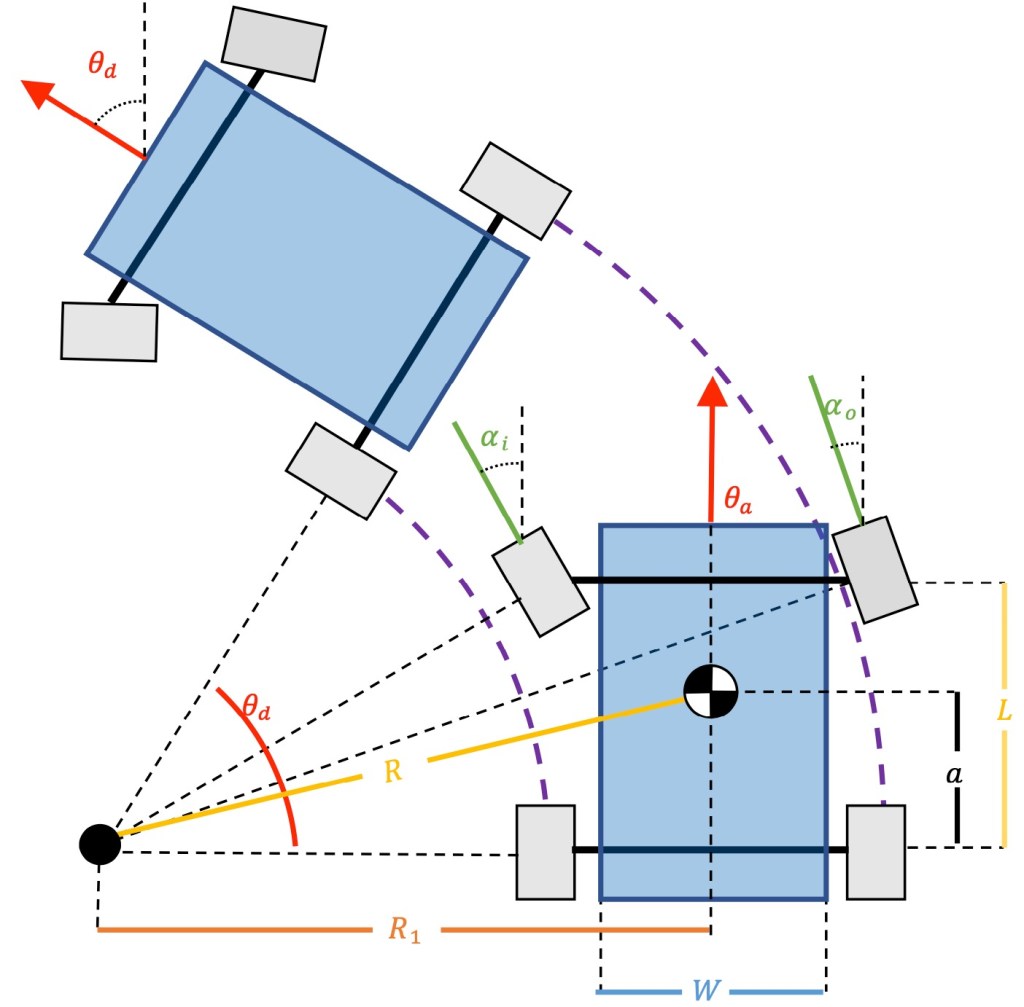
Ackermann Steering PID Controller
For this project we implemented a controller that uses the Ackermann kinematic steering equations.
The Ackermann equations assume that a four wheeled vehicle travels around an instantaneous center of curvature and can compute the kinematics for given turning angles for both the inner and outer wheels. The basic idea behind Ackermann steering is that the inner wheel should steer for a bigger angle when compared to the outer wheel.
This stops the wheels from slipping side ways when the vehicle follows a curved path. We are assuming that the controller is for a four wheeled robot with front-wheel steering and rear-wheel drive.
This project was completed using AIP with the involvement of 3 programmers using Pair-programming in turns.
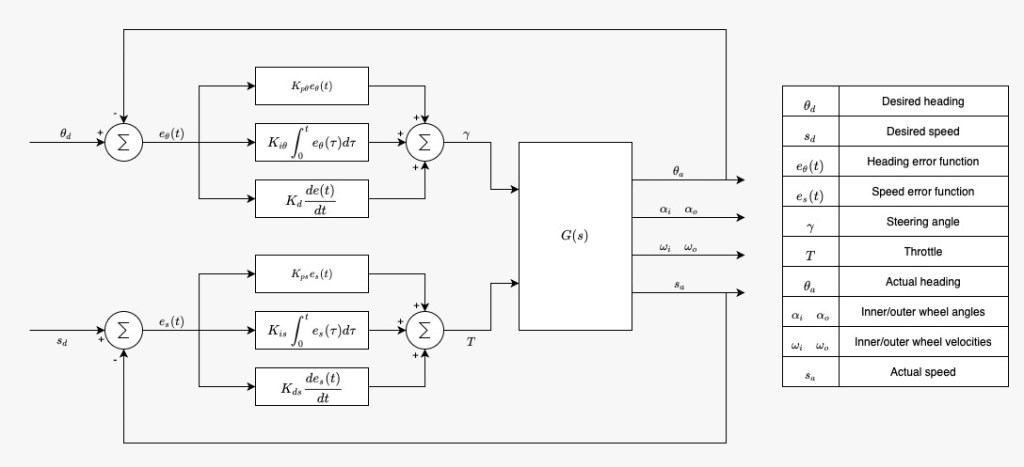
The controller developed is a PID Controller. The system layout can be seen here:
All the code has been documented well on my GitHub repository linked below.
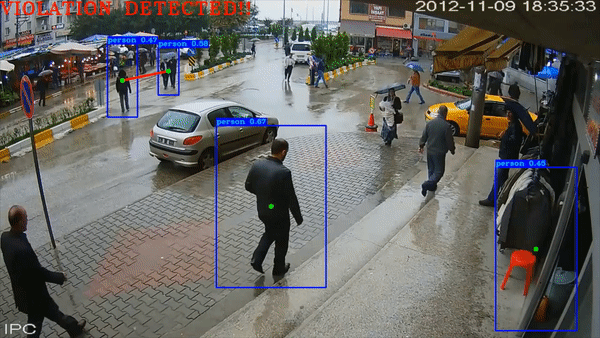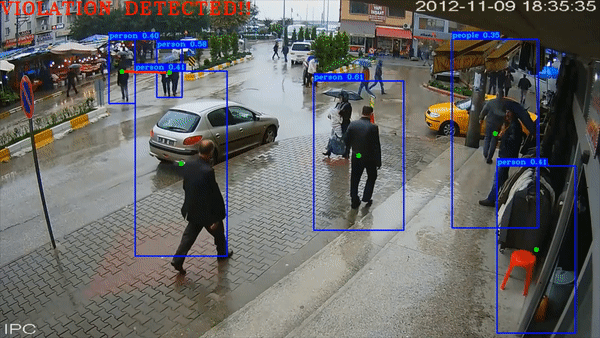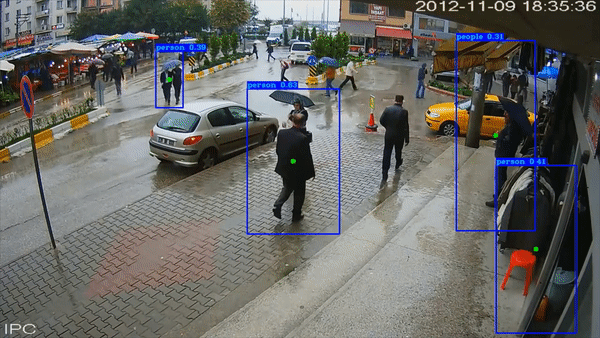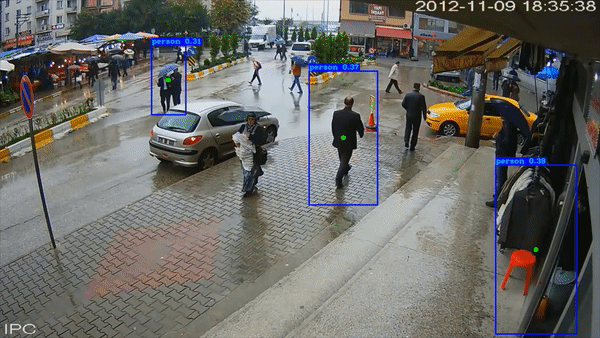
Social Distance Checker
The project was a self-project that I decided to do. The programme checks for social distancing among subjects (trained for pedestrians) in a COVID World.
All the code has been documented well on my GitHub repository linked at the button below.

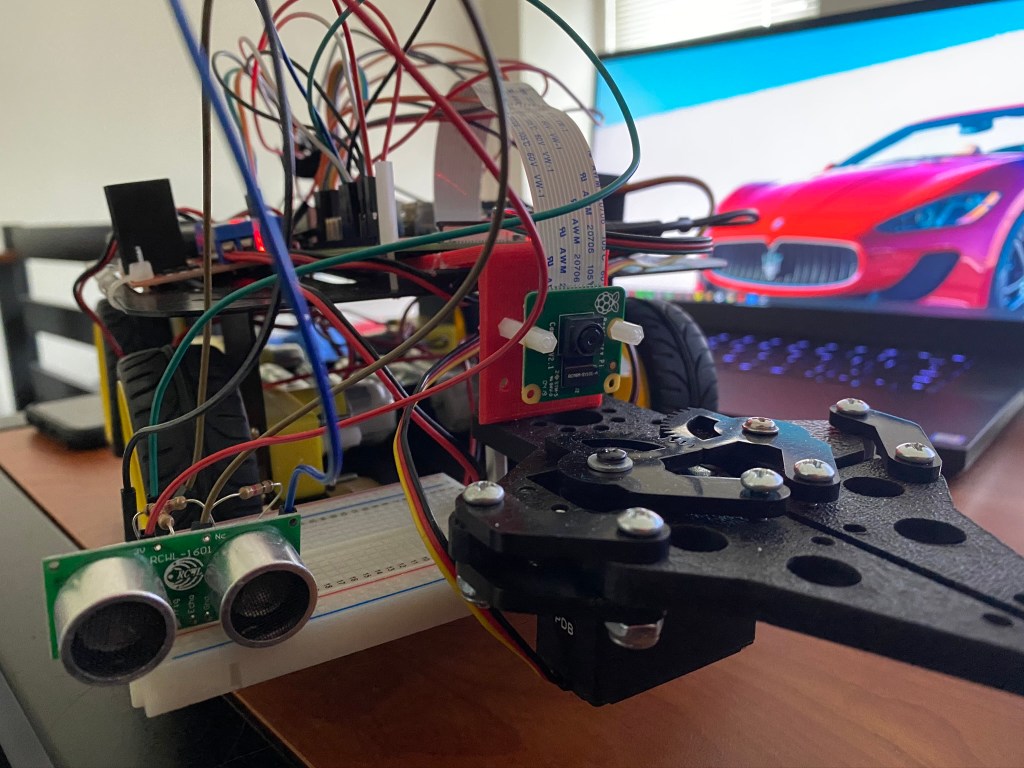
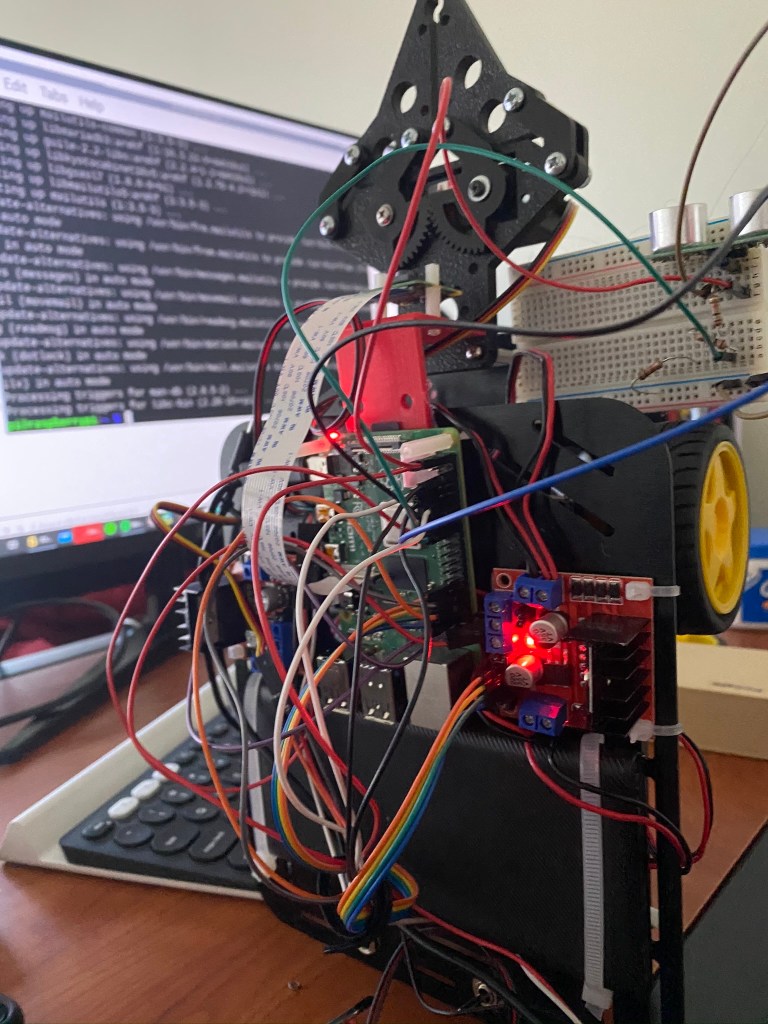
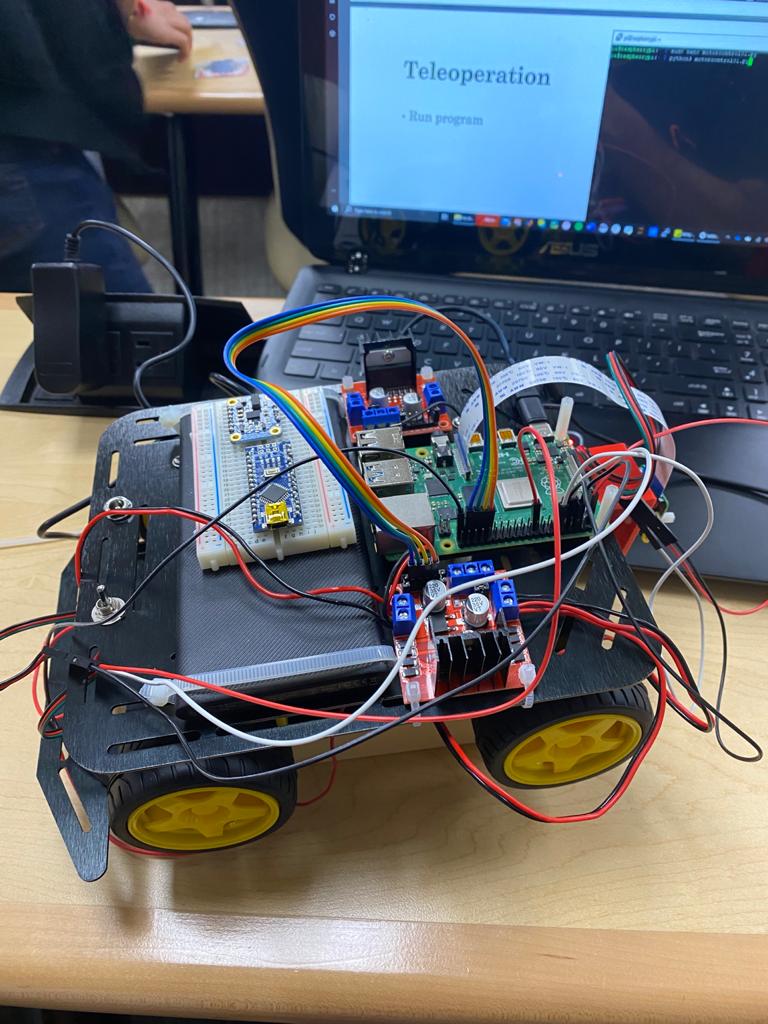
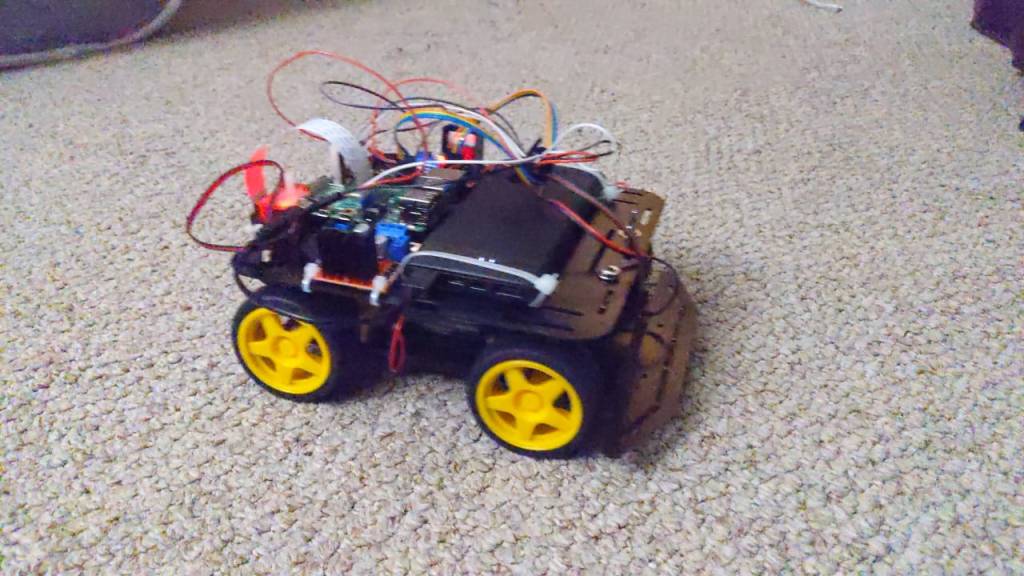
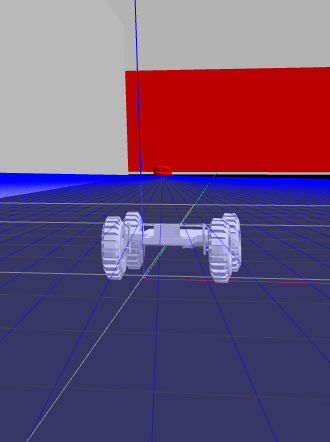
Autonomous Ground Robot
The robot was build as part of the Autonomous Robotics course taught at the University of Maryland. The project spanned over 6 months and has been a steep learning curve in fields of planning, perception and kinematics.
The entire build of the robot can be seen by clicking the button down below.
All the codes for the project can be seen by clicking the button down below.
Here are some of the photos of the robot.
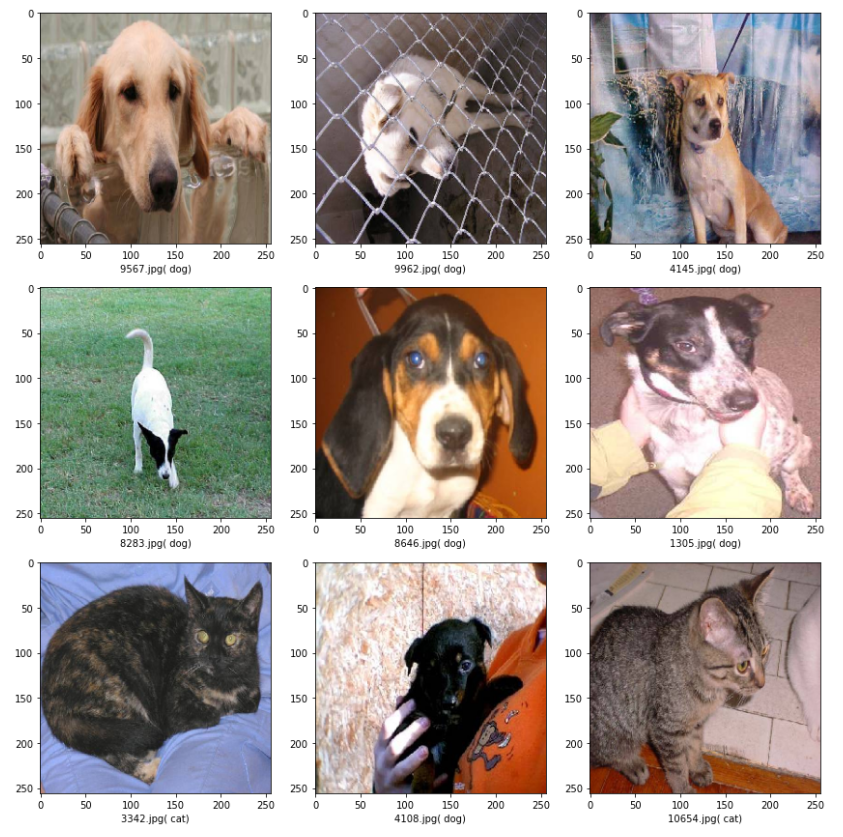

Kagle Challenge : Machine Learning | Classifying Dogs and Cats
The challenge was to classify a set of images as Dogs or Cats using Convolution Neural Networks. The link to this challenge can be found here:
The project used Tensorflow GPU, Cuda 10.2 and was coded on a NVIDIA RTX 2060 equipped Razer Blade laptop.
The graphs depicting the final result can be seen here:
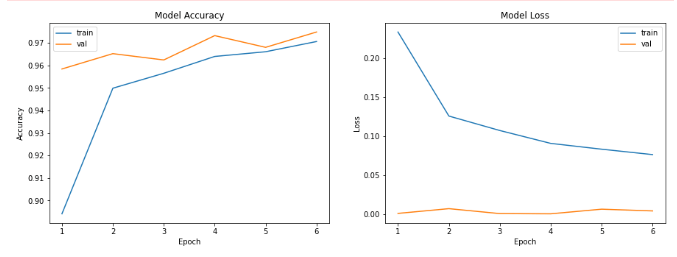
I was able to attain a final testing accuracy > 96.5 – 97 percent, on various runs.
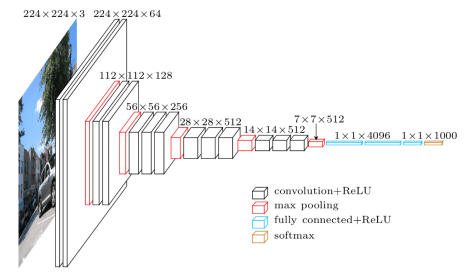
The project used a VGG 16 Architecture as well. You can see how the architecture is laid out in the image below.
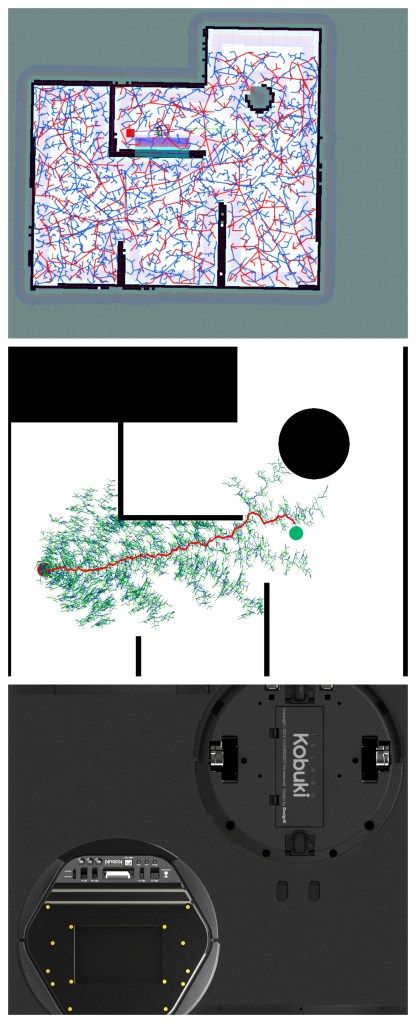
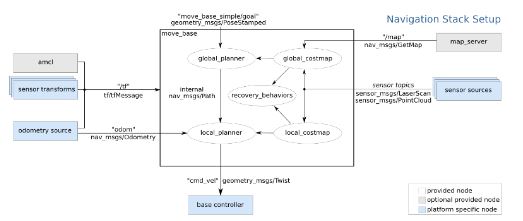
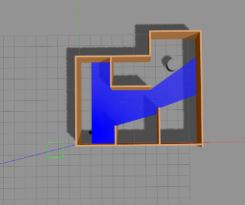
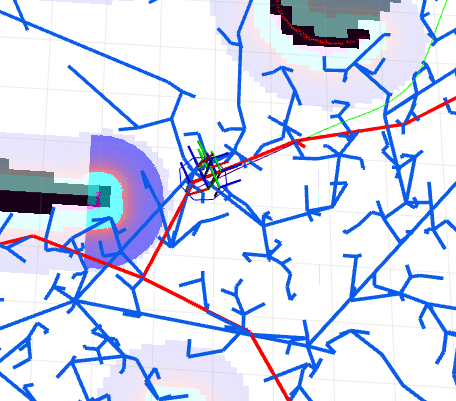
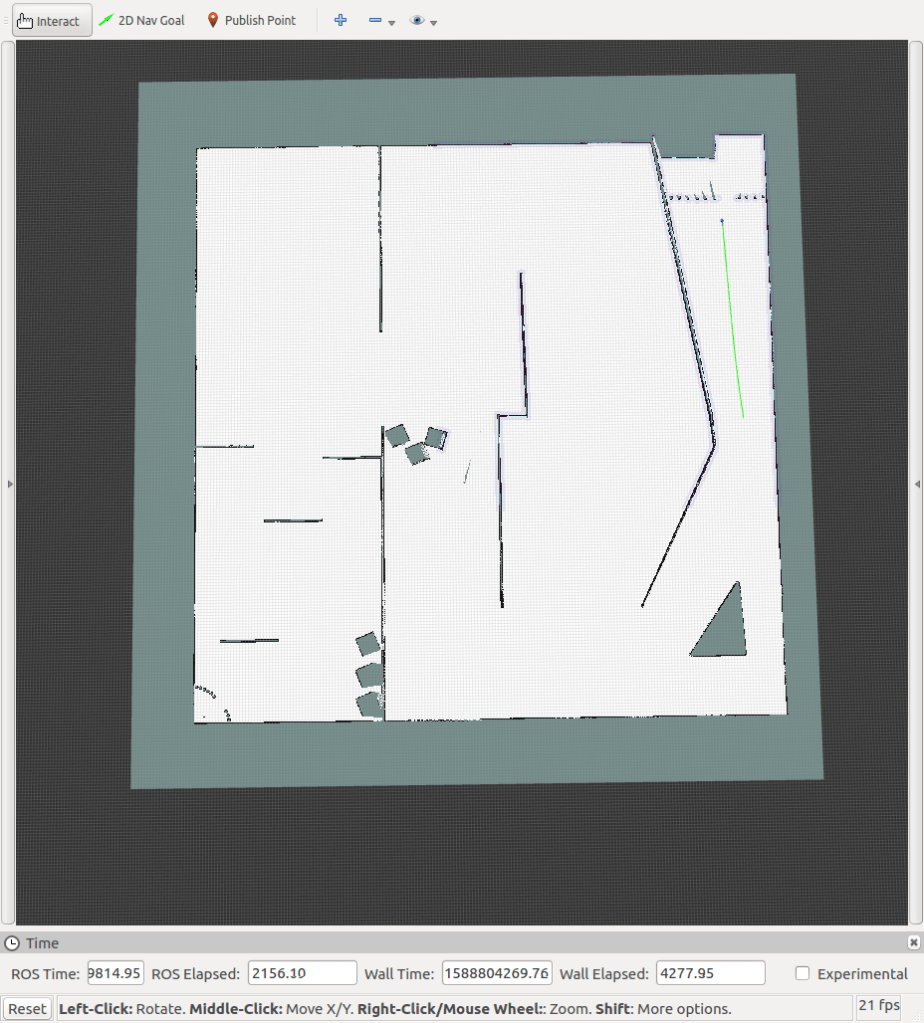
Robot navigation and path planning using SLAM, RRT and RRT*
The project consisted of moving a Kobuki iCelebo through a predefined world map. The robot calculates the path using the concepts of Rapidly expanding Random Tree (RRT).

SLAM is performed to localize the robot in the world. I used gmapping in ROS Kinetic for attaining the map. The local cost maps, global cost maps, obstacles, and path that has been detected by the LIDAR attached to the robot can be seen here below.
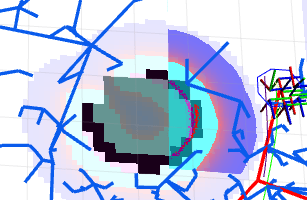
Black – Definitive boundaries
Vivid purple – Local cost map
Light purple – Global cost map
Red dots – LASER scan
The final map that was generated from the start to the goal can be seen on the left side. The simulations were also performed on Python and can be seen below.
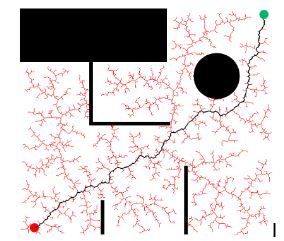
RRT Simulation 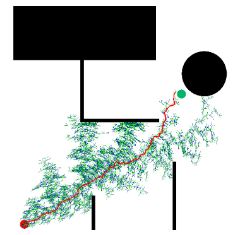
RRT* Simulation
The above simulations can be seen live down below
The final simulation done on RViz and Gazebo can be sen here down below:
Please also find a final report of the project at the same link. All other relevant images for any further information is also attached here down below.
Robot controller and LIDAR implementation using ROS
The project was a part of the final challenge in the course Planning for Autonomous Robotics.
I added a effort controller for positioning of the wheel, velocity controller for control of the velocity of the robot itself.
The entire arena, which was over 50 meters long was also mapped using SLAM and an image of this can be seen below.
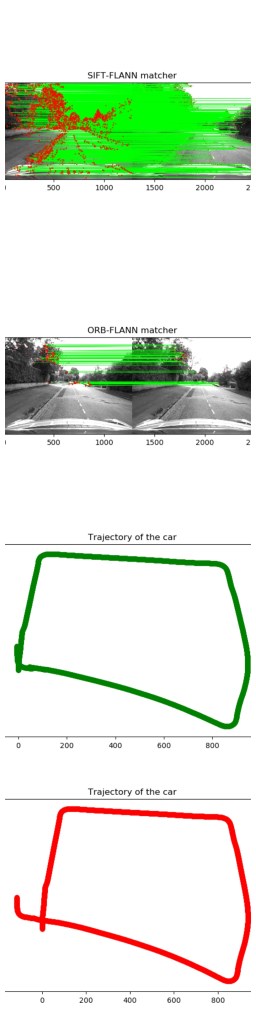
Visual Odometry | Structure from motion
The project dealt with tracking the path followed by car using Visual odometry. The key points in the image was detected using ORB feature detector and SIFT feature detector.
The key point detection can be compared in the image below.
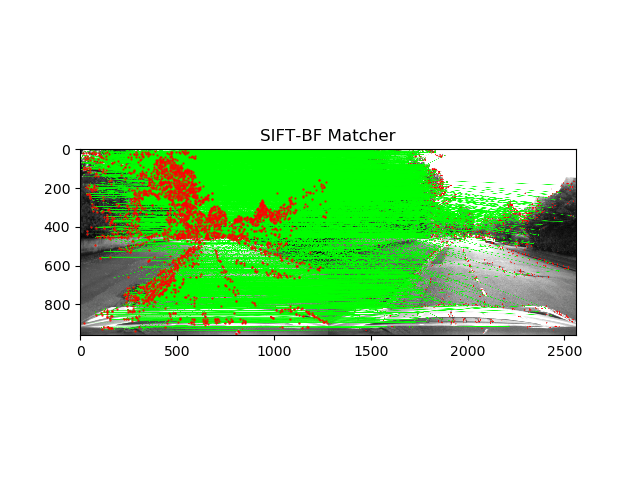
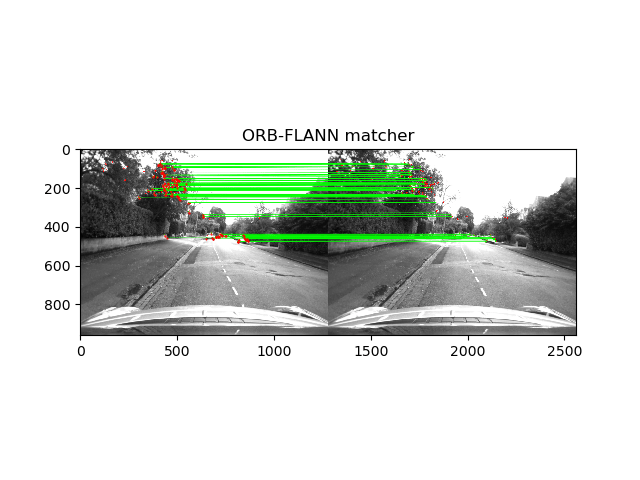
As you can see, the SIFT feature detector gave much better results. We used FLANN matcher for ORB key-point detection and BF matcher for SIFT respectively.
The plots + SIFT feature detection over time can be seen in the video below:
The final result can be seen below. This map was generated using user developed and defined functions.
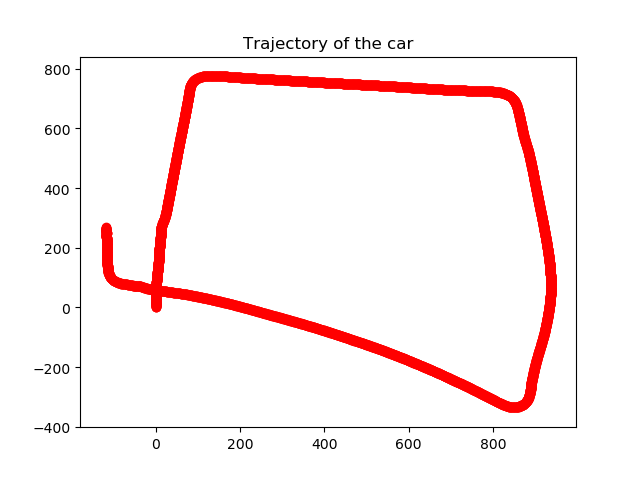
A video depicting how this plot was generated can be seen here.
The comparison was also drawn with in built functions to generate a path and the final result can be seen below.
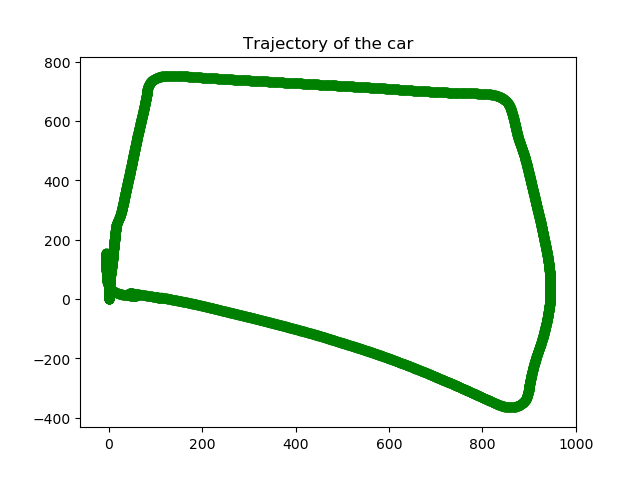
A video depicting how both plot was generated and their differences can be seen down below.

Object Tracking using Lucas Kanade Affine Algorithm
The project was an exercise in object tracking using Lucas Kanade Algorithm. The algorithm checks for motion of the pixels and helps in tracking the object through space.
The tracking gets challenging when it is required to track a fast moving object, or anything under dimly illuminated conditions.
Here we track a moving car which is changing lanes, Usain Bolt and a baby fighting a dragon.
Please find the videos down below
In the video below you can see that the path is filled with shadows from the trees as well as from the bridge. Hence, it is pertinent to do brightness correction. This is one of the conditions where Lucas Kanade breaks down. You can see two videos Down Below. First, without brightness correction:
Second video down below has brightness correction. You can see it here down below:

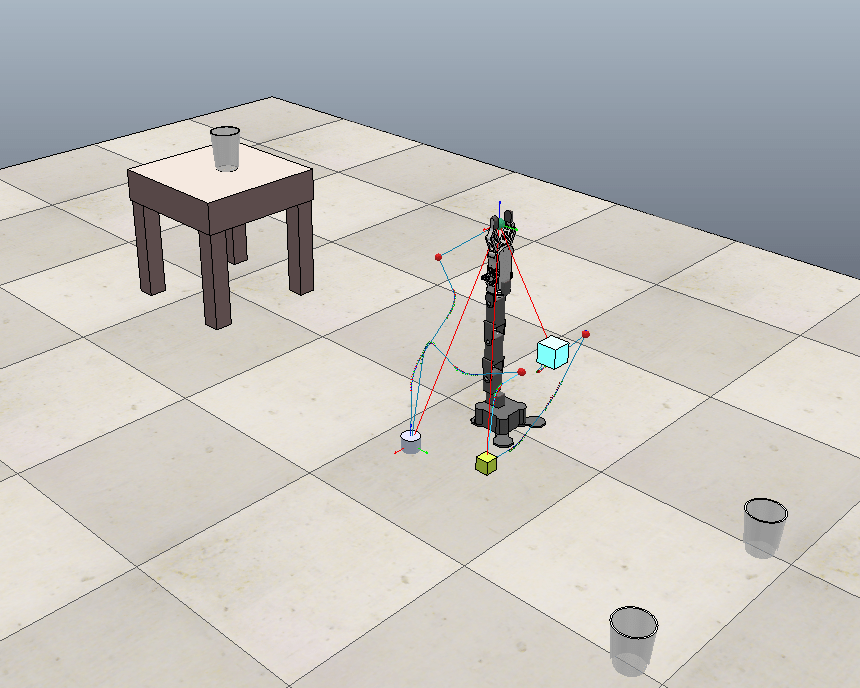
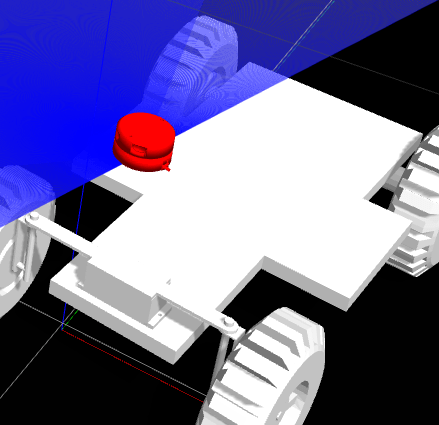
Baxter Arm Pick and Place on Gazebo using ROS, OMPL, MoveIt, RViz
The project works with ROS and Baxter. The task was to pick the Red box and place it on the adjacent table, followed by picking up the white box and placing it on the adjacent table from which the red was picked.
At the same time, it was imperative to avoid obstacles along the way. This was planned using the OMPL Library.
Successfully picked and placed two objects by avoiding obstacles.
OMPL Libraries used along with Moveit ROS Framework. The top view of the full solution can be seen here,
Please find result down below.
Rviz 
Pick and Place

Turtlebot obstacle avoidance using A* Algorithm
The simulation moves a turtlebot from one point in an obstacle space to another.
Simulation was done and visualized in Gazebo through ROS and Python. This is a continuation of a project linked down below.
Please find some working videos under various test conditions down below.

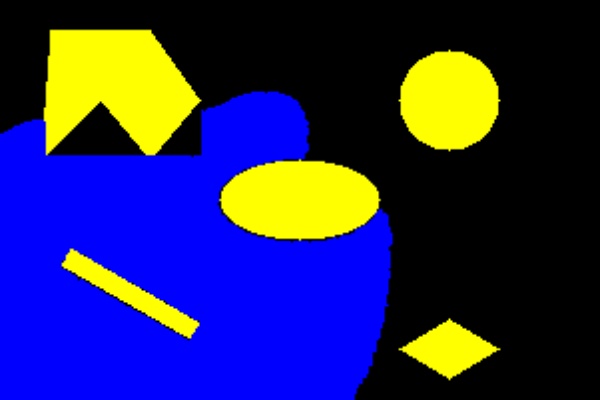
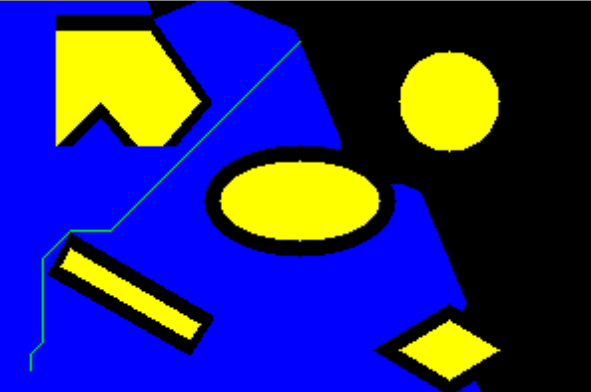
Image Color segmentation using Gaussian Mixture Modelling and Expectation Maximization
The project, coded in Python segments image using the concepts of Gaussian Mixture modelling.
This concept helps in image segmentation in challenging lighting conditions, such as the one seen here.
An original video, which was the problem statement is depicted down below. Here, the task is to detect the buoys both individually and in a combined video as well.
Codes have been written for all of them in Python 3 and implementing OpenCV as well and can be viewed by clicking the button below.
The videos of the final results that have been achieved by us can be seen here.
Green Buoy detection
Orange Buoy detection
Yellow Buoy detection
Combined Buoys detection
EDIT: Since code has been worked on and an improved detection for the green Buoy is posted here.
Hence, an updated video output for all three combined is obtained as well.
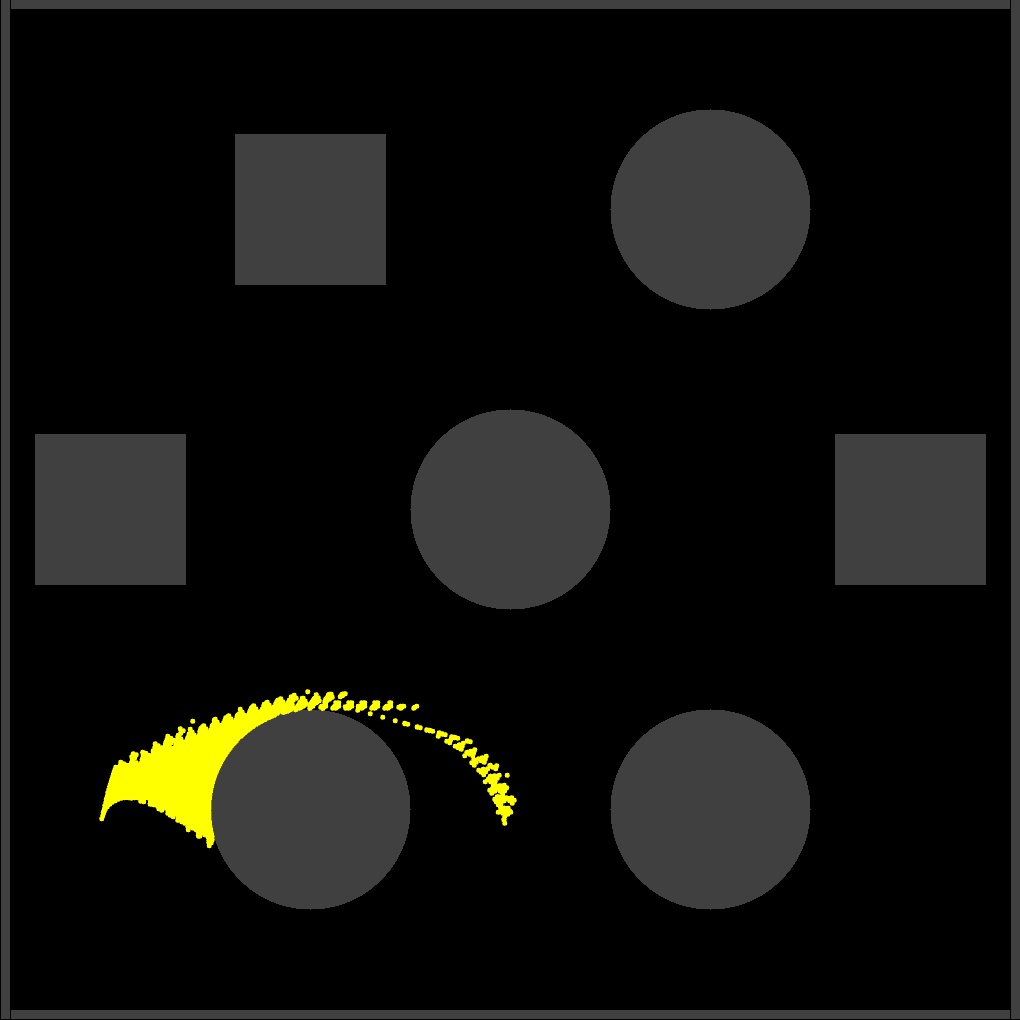
Solving obstacle space by movement from start to goal using the A* Algorithm (for non-holonomic Robot)
This program solves the obstacle space for a non-holonomic Robot.
The formula by which the wheel velocities are mentioned are here below.
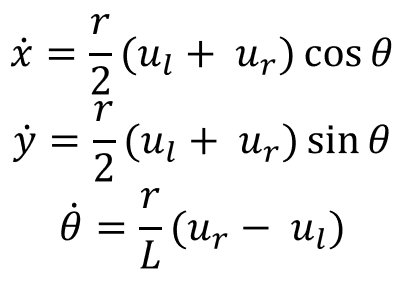
From the above formulae for velocities, the distance traveled by the robot can be found below.
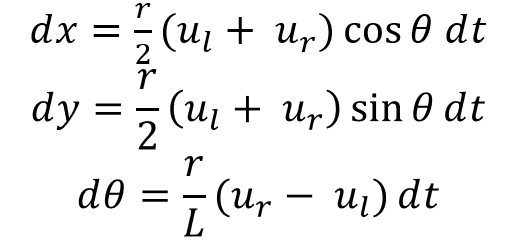

Backtracked Path 
Obstacle space 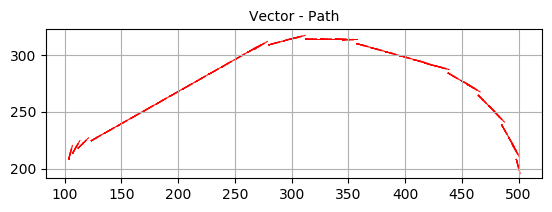
QUiver map, showing the visited nodes 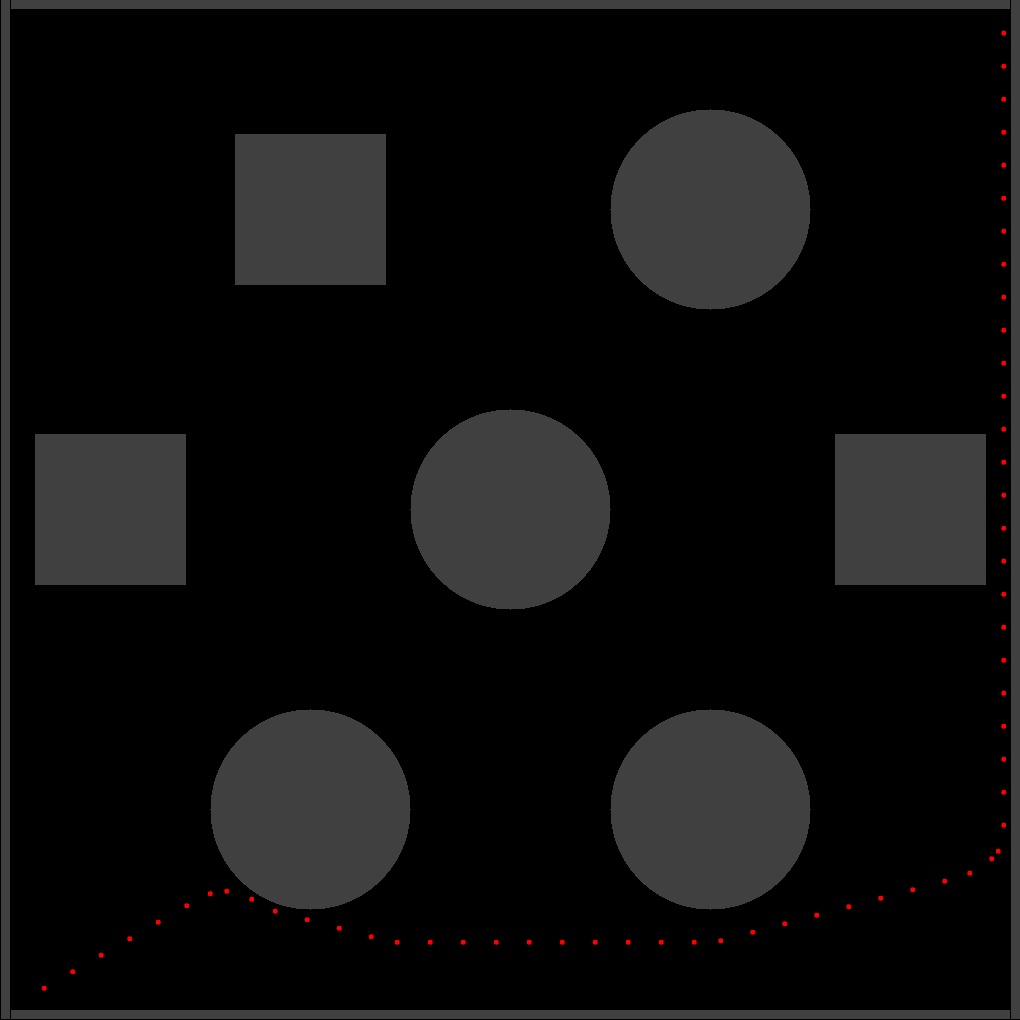
Backtracked – Test case 2 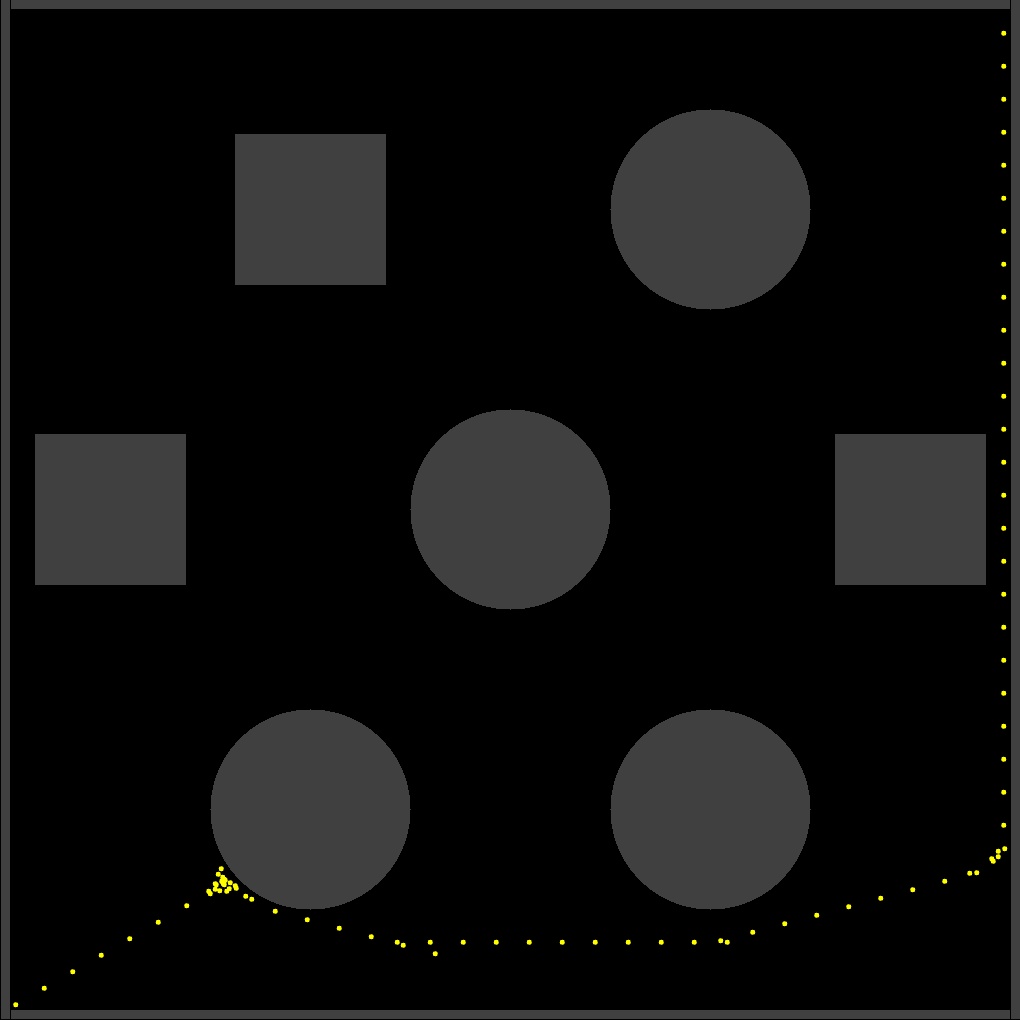
Visited Nodes – – Test case 2 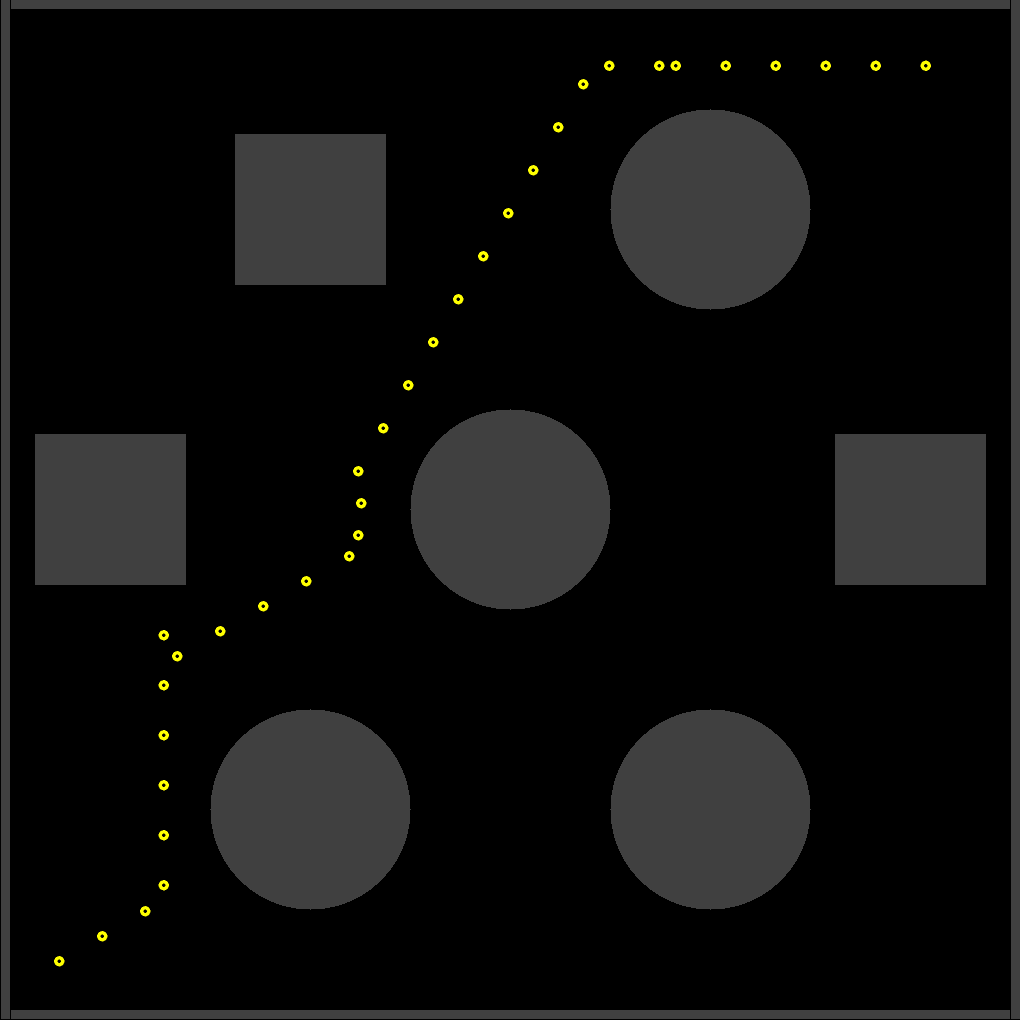
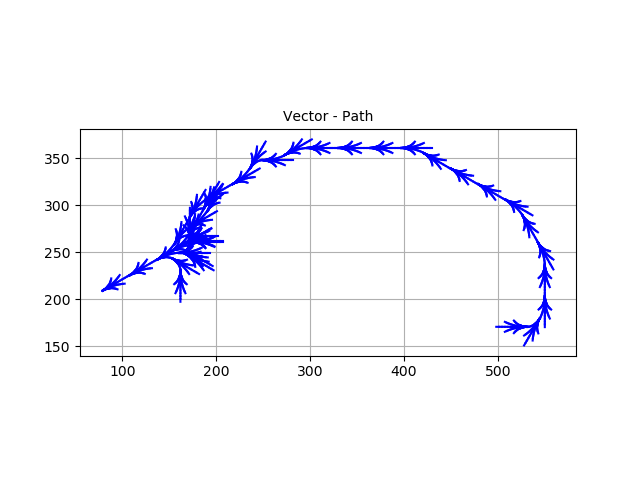
Quiver plot – better look 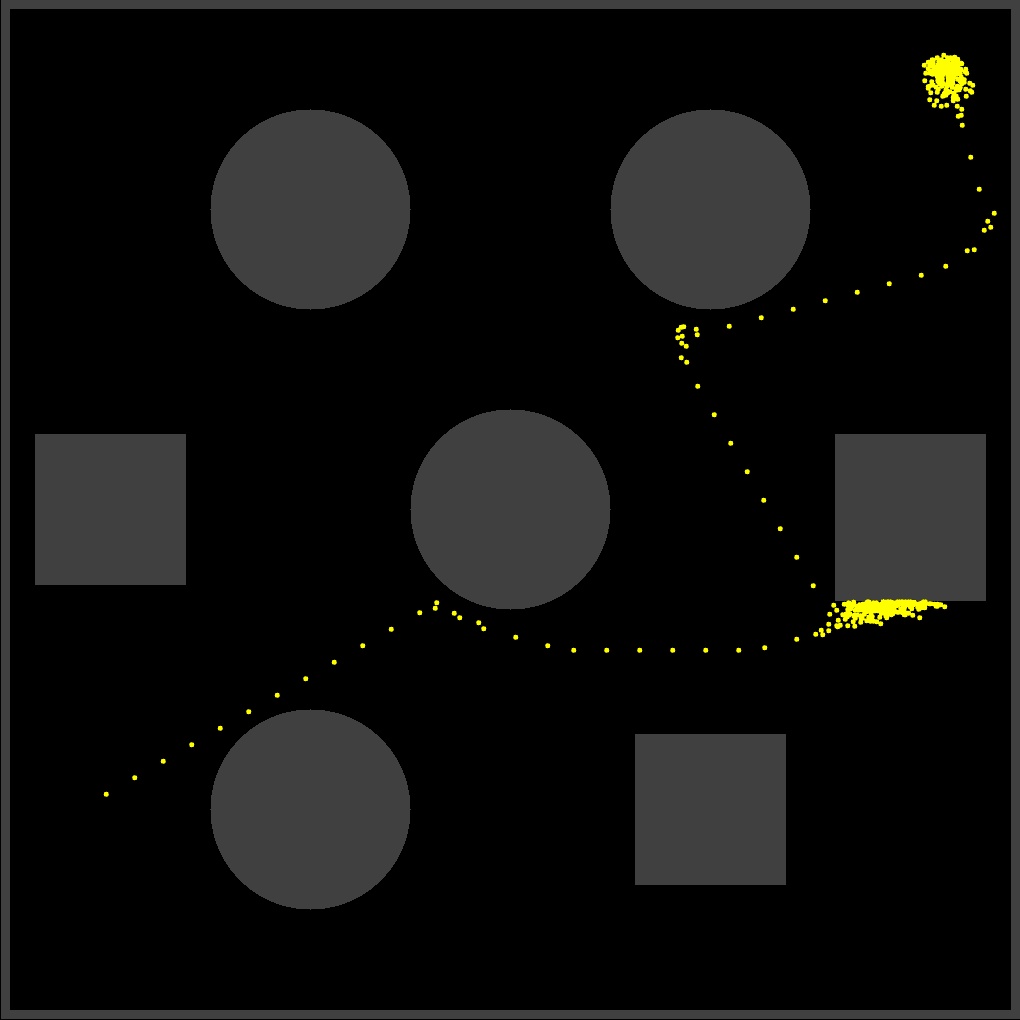
Path solution
Please see the Youtube Video here, as soon as it is uploaded (in 6 days or less).
Project has been implemented on a Turtlebot on Gazebo using ROS. Please see above.
The links to the solution here can be seen here down below:
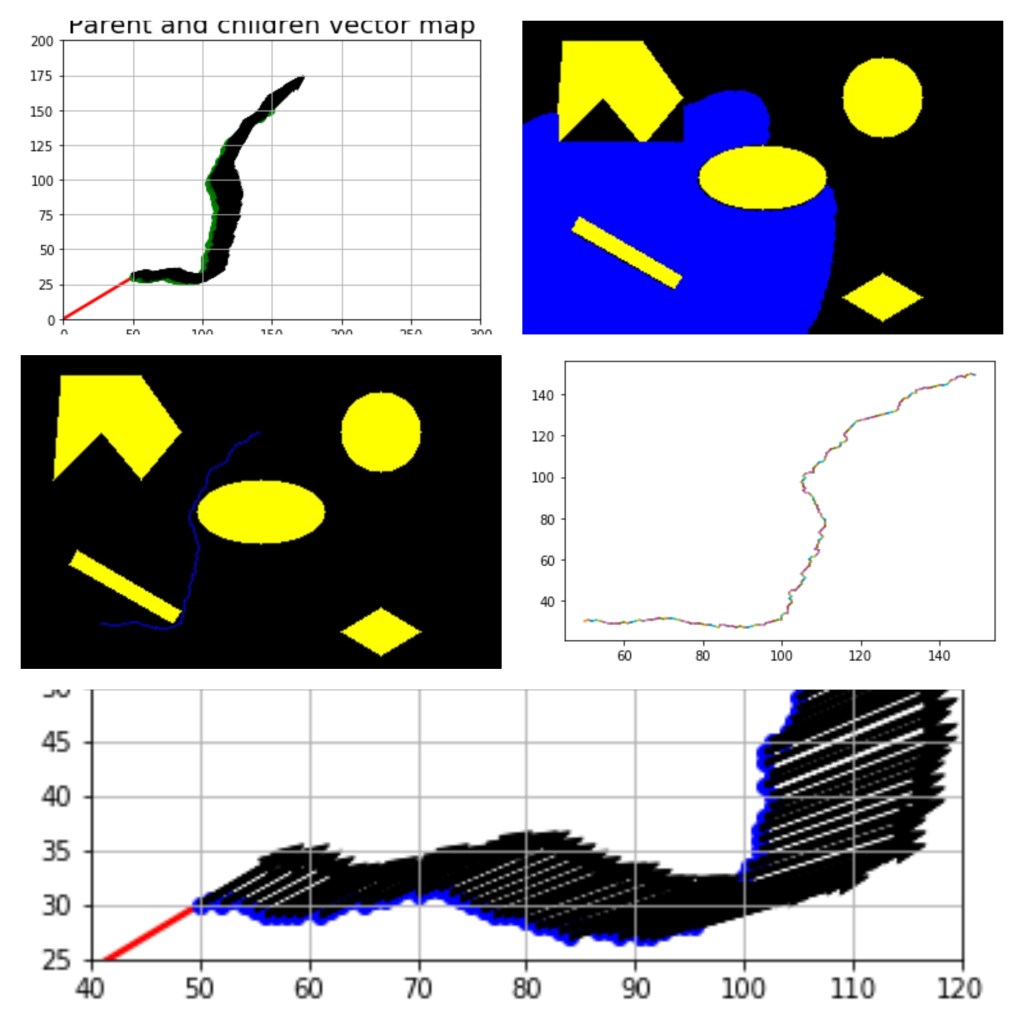
Solving obstacle space by movement from start to goal using the A* Algorithm (for Rigid Robots)
In the below images, notice the difference in the area explored by Dijkstra and A* algorithm. Here you can see how much lesser area is explored by the A* algorithm as compared to the Dijkstra.
Please visit my github repo for additional information on the A* converted from Dijkstra as shown here.
This basic modification wasa followed by added constraints of motion, where the robot was allowed to move in 5 degrees of motion only (-60 degrees, -30 degrees , 0 degrees, 30 degrees, 60 degrees) with step size between 1 and 10. A robot is allowed any starting point within the parameters of the obstacle space. The user also chooses a goal point within the obstacle space.
The obstacle space is pre-defined here. However, the algorithm will work for any case.
The input conditions are shown here.
Below image shows the path traversed and backtracked using A*
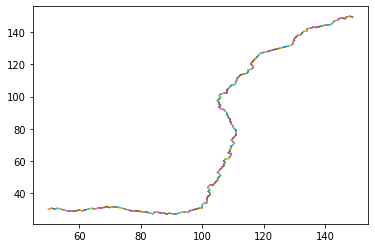
Click on the images to see the visited area and the path backtracked.
Please find the code for the above project on my Github Repo here (under the folder named Old Submission), and the video can be found below.
EDIT:
The code was edited for a better result. The new code can be found in the same repository as linked above. The improved video is shown below.
The time was reduced from 30 minutes to 21 minutes.
Also attached a new folder, with an alternative method, where we found a much faster solution
TIME TAKEN : < 1 minute
You can find the alternative path video down below.
EDIT: A newer code was developed and the solution time changed drastically. Now the solution is obtained in 0.6 seconds, a massive reduction from 21 minutes.

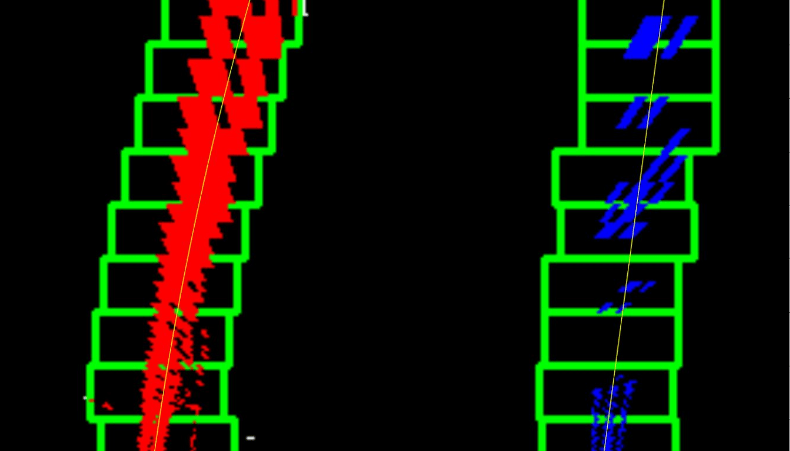
Lane detection along a curved path using OpenCV and direction detection
Performed lane detection and indicated the detected lane along the curved path.
Challenges here included the multiple objects, white and yellow cars, shadows, a bridge and anything that could represent a straight line.
The final outcome of the code can be seen here below.

Lane detection along a straight path using OpenCV
Performed lane detection and indicated the detected lane along the path.
A video of it can be seen here below
Challenges here included the multiple objects, white cars, shadows and anything that could represent a straight line.

Night time video enhancement of a feed from an autonomous vehicle using CLAHE and histogram equalization
A dark video with little visibility was enhanced for better viewing through the night.
The original video can be seen here. Notice the improved details.
Just for reference many other methods were also tried, shown in the images below. Do notice the excessive noise that occurs in many cases.

CLAHE and HSV (done above) is decided to be the best solution 
CLAHE 
Gamma and equalized Histogram 
Gamma only
Solving obstacle space by movement from start to goal using the Dijkstra’s Algorithm (for point and Rigid Robots)
A robot is allowed any starting point within the parameters of the obstacle space. The user also chooses a goal point within the obstacle space.
In case of the rigid robot, the user is also allowed to choose clearances and the radius of the robot.
The obstacle space is pre-defined here. However, the algorithm will work for any case.
Video can be found below.
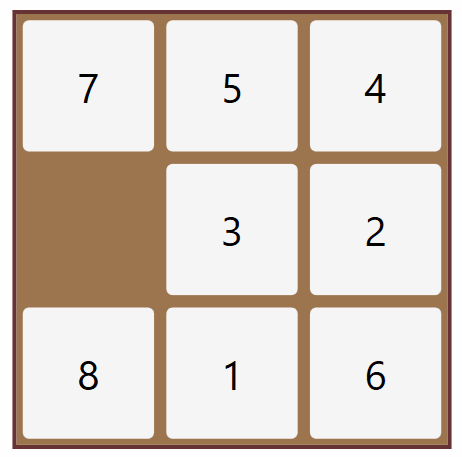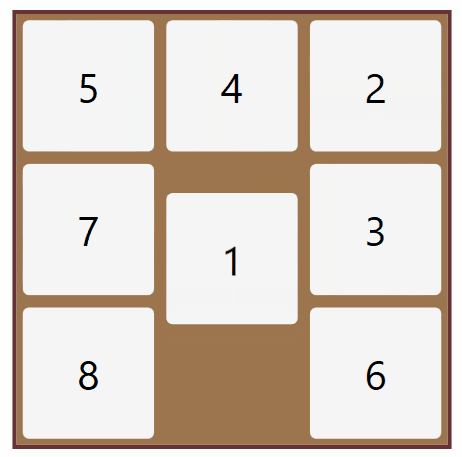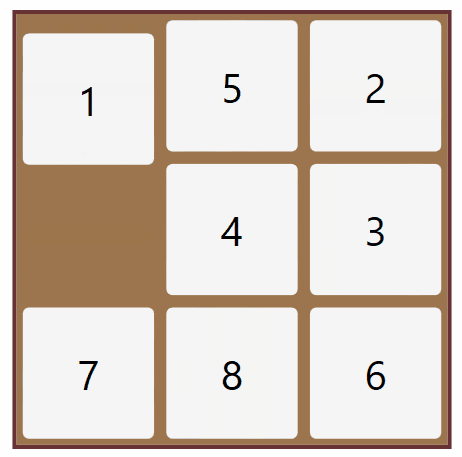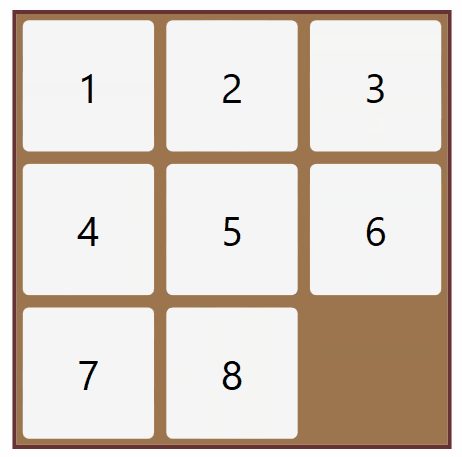
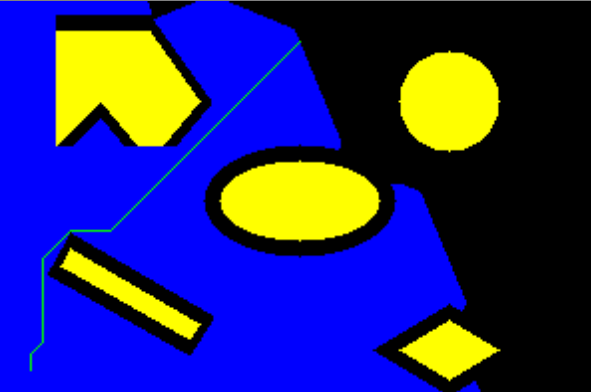
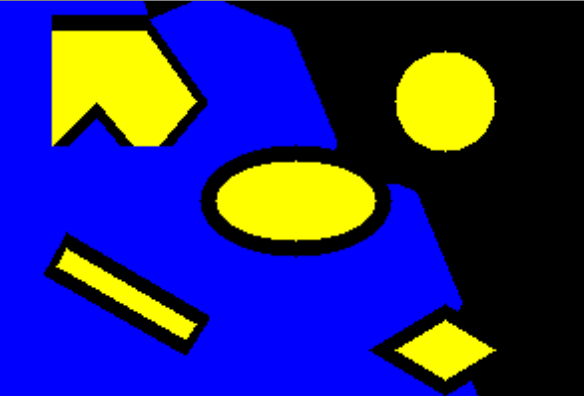
Solution of the 8 Puzzle problem using Brute Force Search Method
Python 3 scripting to solve the 8 puzzle problem.
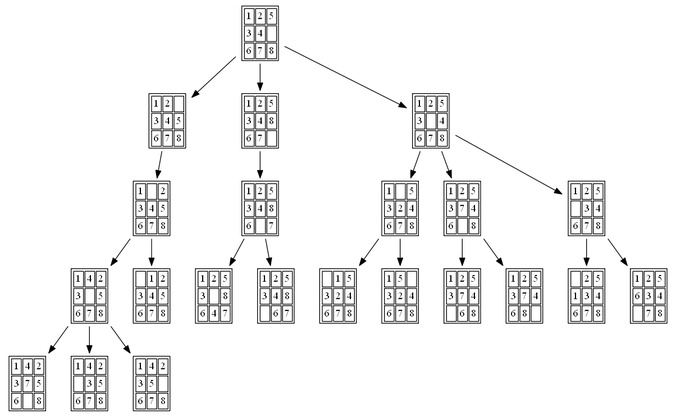
Efficiently solved from any user defined start to user defined goal.
Checked for solvability case.

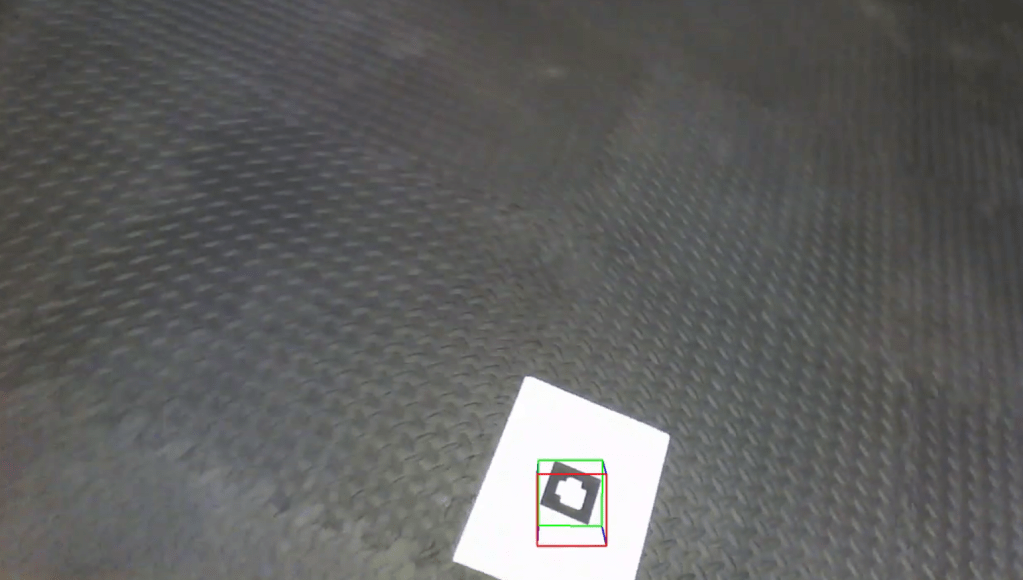
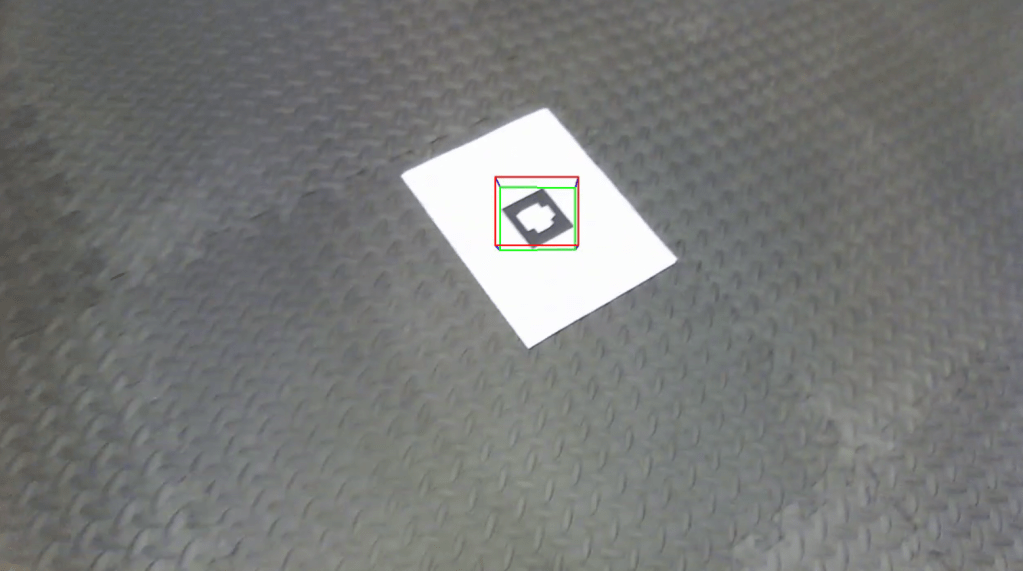
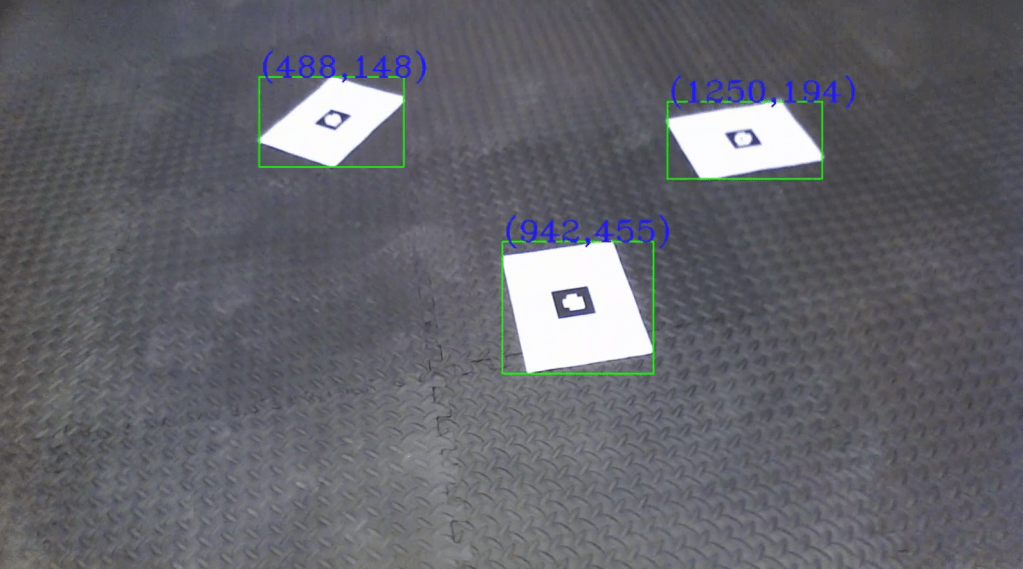
Detection of AR Tags, image super-imposition, cube super-imposition and Tag ID Decoding
The project involves the detection of AR Tags, decoding the tag ID for three different tags.
Also superimposed the famous ‘Lena’ on the tags and was able to rotate it using Homography and warpPerspective.
Developed a ‘warpPerspective’ algorithm to replace the cv2.warPerspective. Also developed a ‘findHomography’ algorithm, to find the AR Tag orientation.
Developed a code to detect the AR Tag and place a virtual cube on the image as well. The cubes are seen to move when the camera angle changes, using the concepts of camera pose estimation.
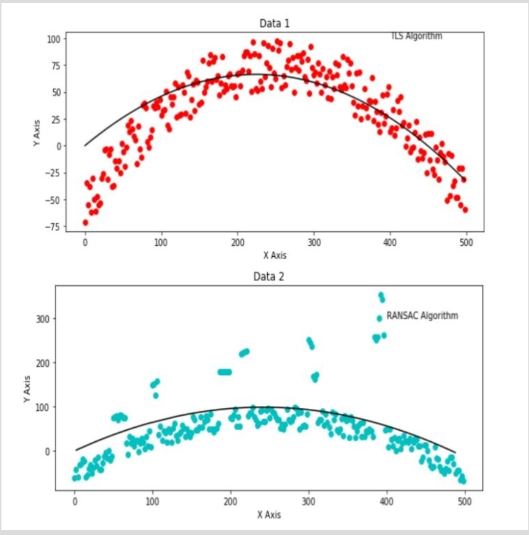
Curve Fitting using self-developed RANSAC and Least square method
Developed an algorithm from scratch to perform least square curve fitting for a set of data.
Also developed an algorithm for curve fitting using RANSAC. This method is used in the presence of a large number of outliers.
The challenge in this project lied in the fact that the code did not use any inbuilt function to fit the curve. Rather, all functions were developed from scratch.
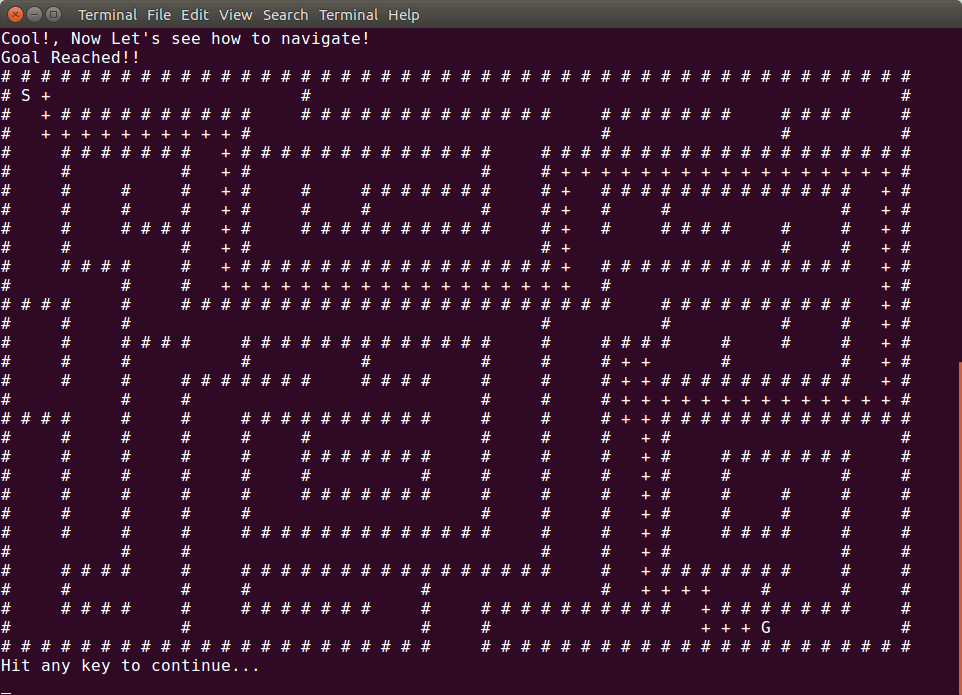
Maze solving using Breadth First search
The code was written in C++.
The mouse can traverse through the entire map and solve the maze using Breadth first search algorithm.
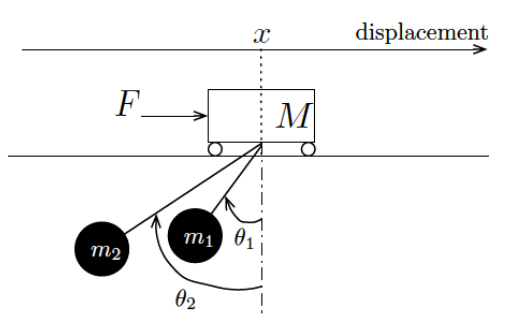
Development of a Luenberger Observer for a moving crane with double pendulum
- Designed and simulated an output feedback controller using the LQG method.
- Performed mathematical checks for controllability, observability and obtained an LQR controller.
- Simulations performed on MATLAB
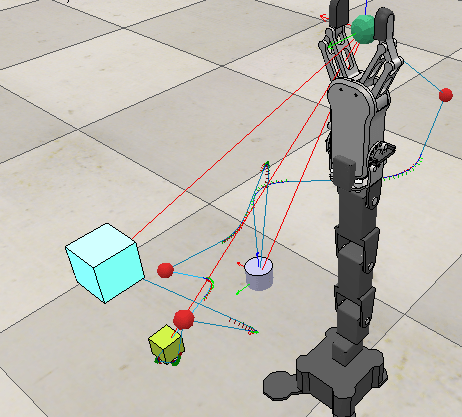
Simulation of a 5-Degree Robotic Arm in V-Rep
- Performed CAD of the manipulator using SolidWorks that can pick and throw objects into baskets placed at various positions.
- Simulated the pick and throw for three objects. Performed Inverse Kinematics & Lua scripting on V-Rep
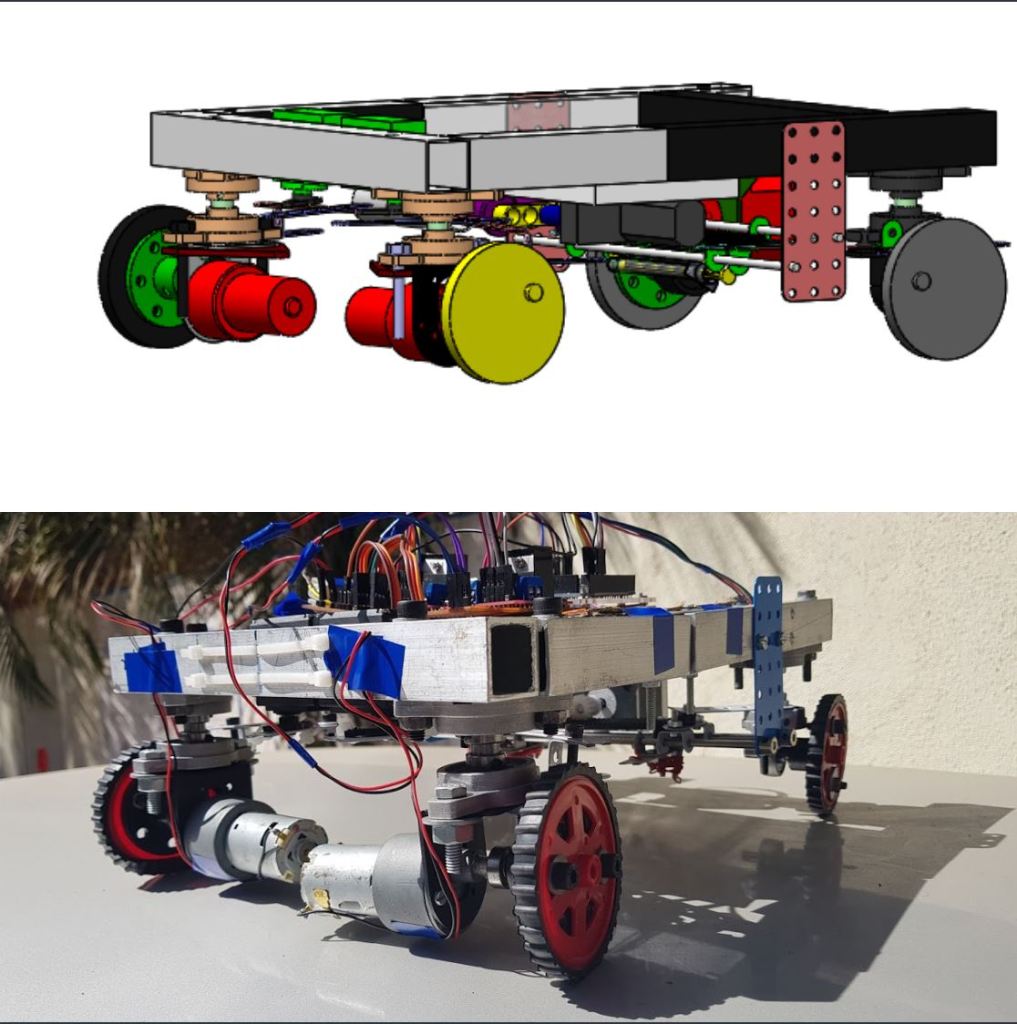
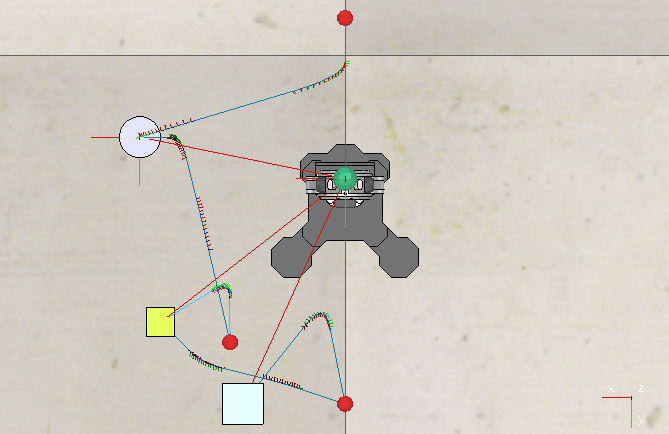
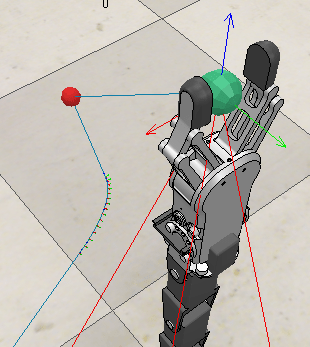
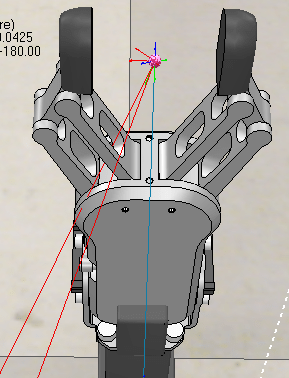
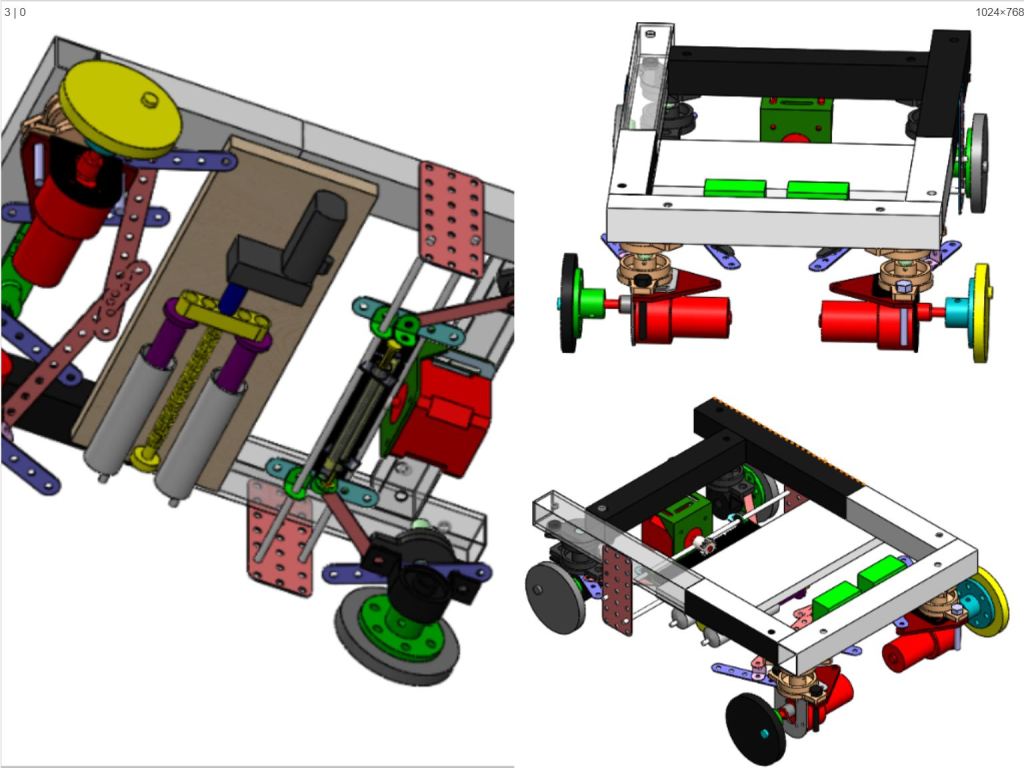
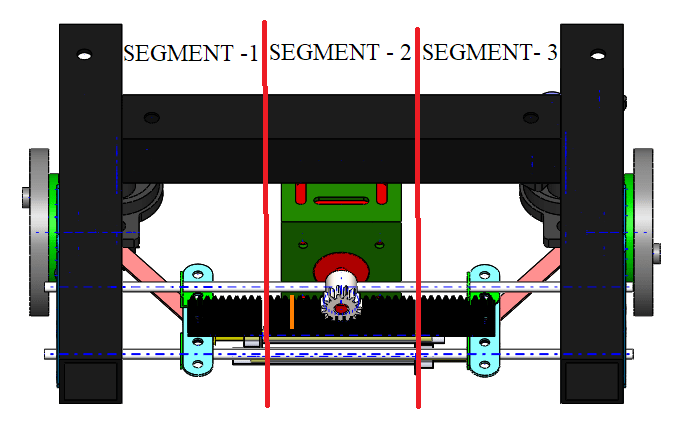
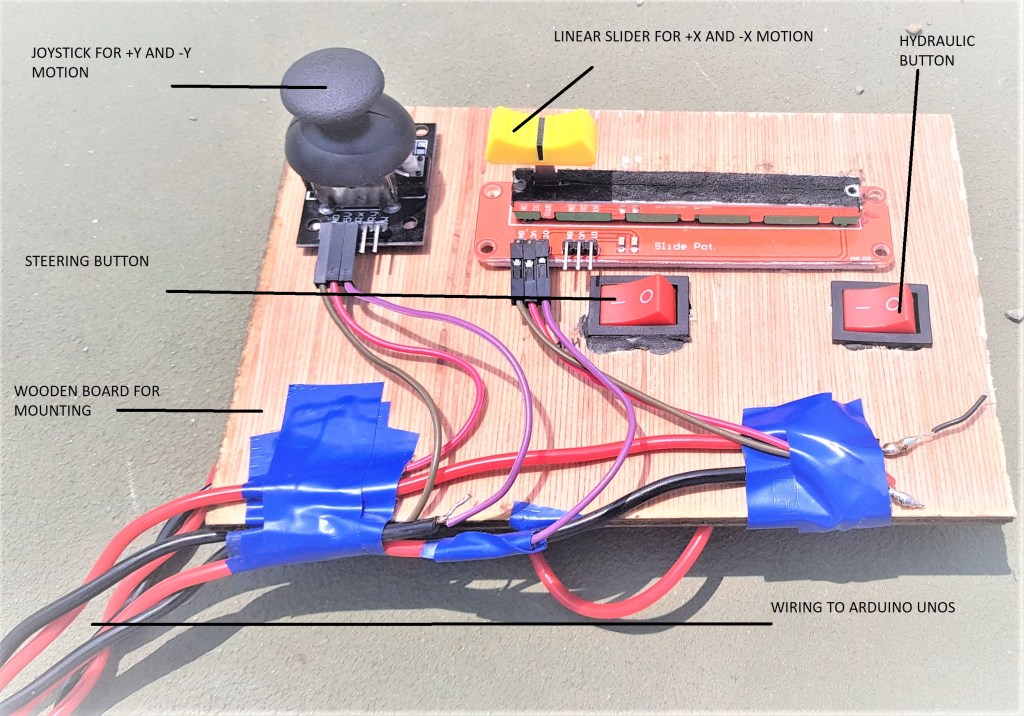
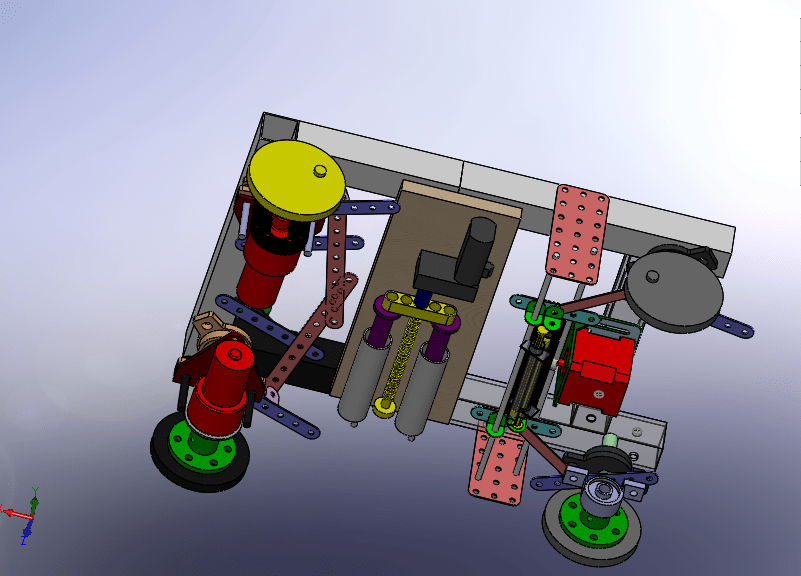
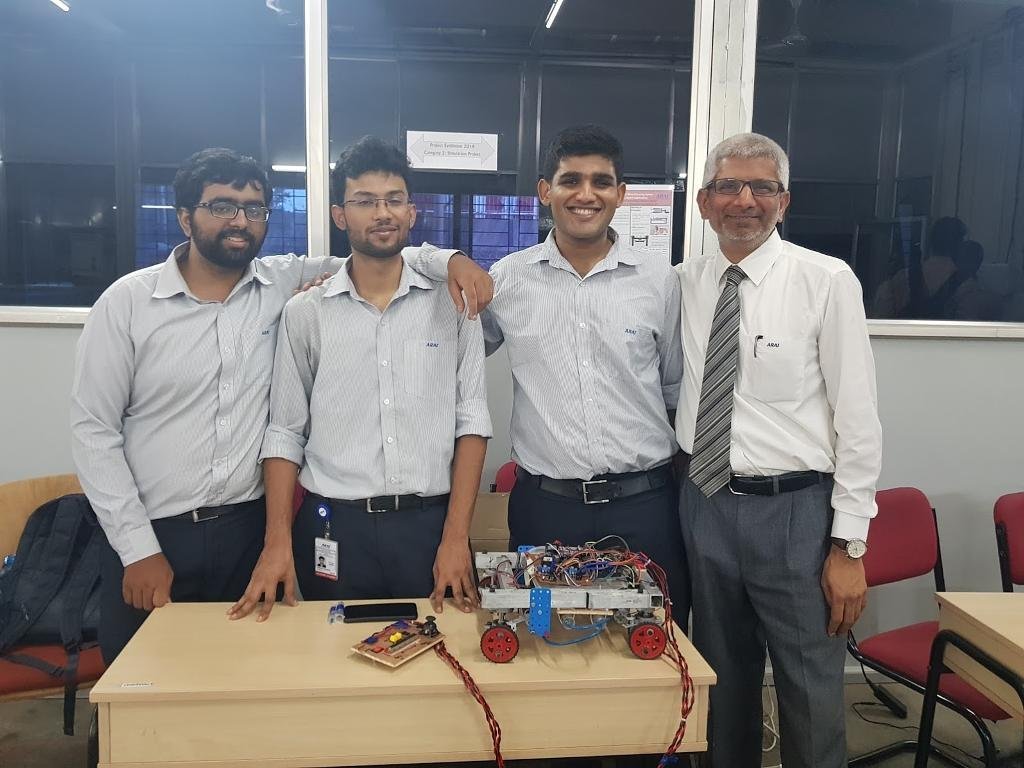
Designed and developed an advanced all wheel steering system for low speed applications
Final year Bachelor in Mechanical Engineering (specialized in Automotive Engineering) Project
- Led the mechanical design and build of a prototype of a vehicle depicting all wheel steering system alongside zero turn steer, thereby virtually reducing the turning circle of the vehicle to zero radius.
- Designed and fabricated a prototype with reduced turning circle radius and incorporated zero turn steer for warehouse, medical and agricultural applications with an average turning radius reduction of 50 % for low speed application
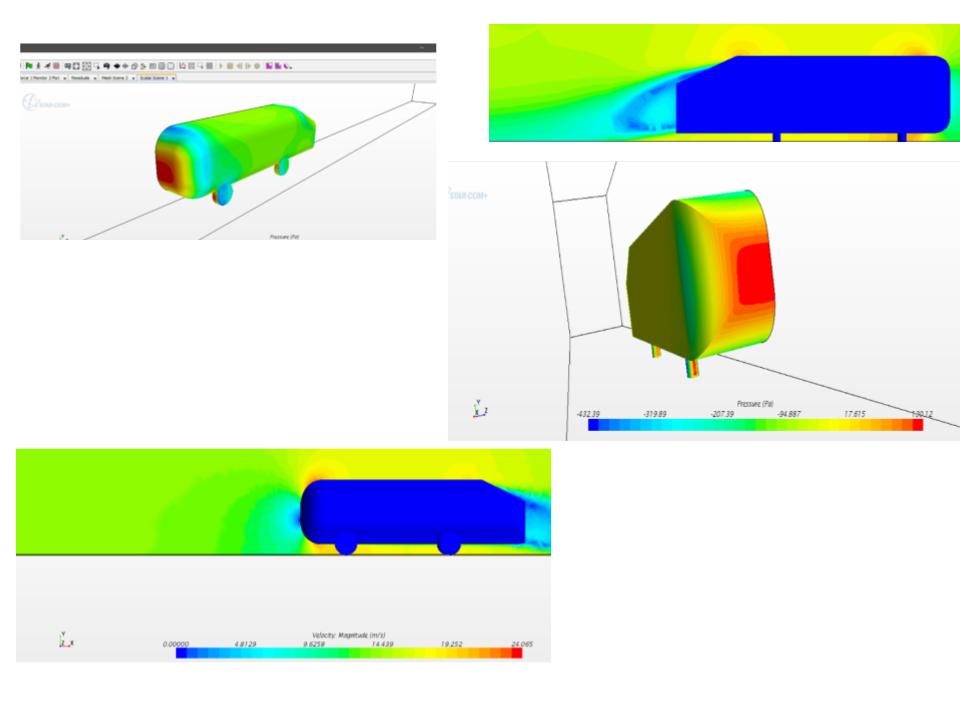
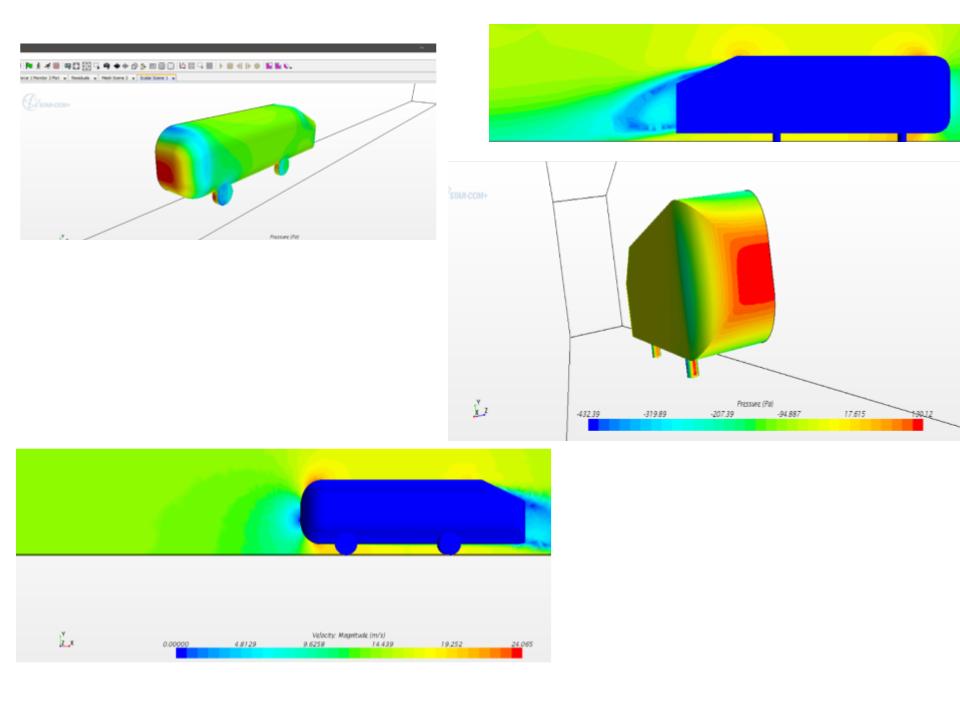
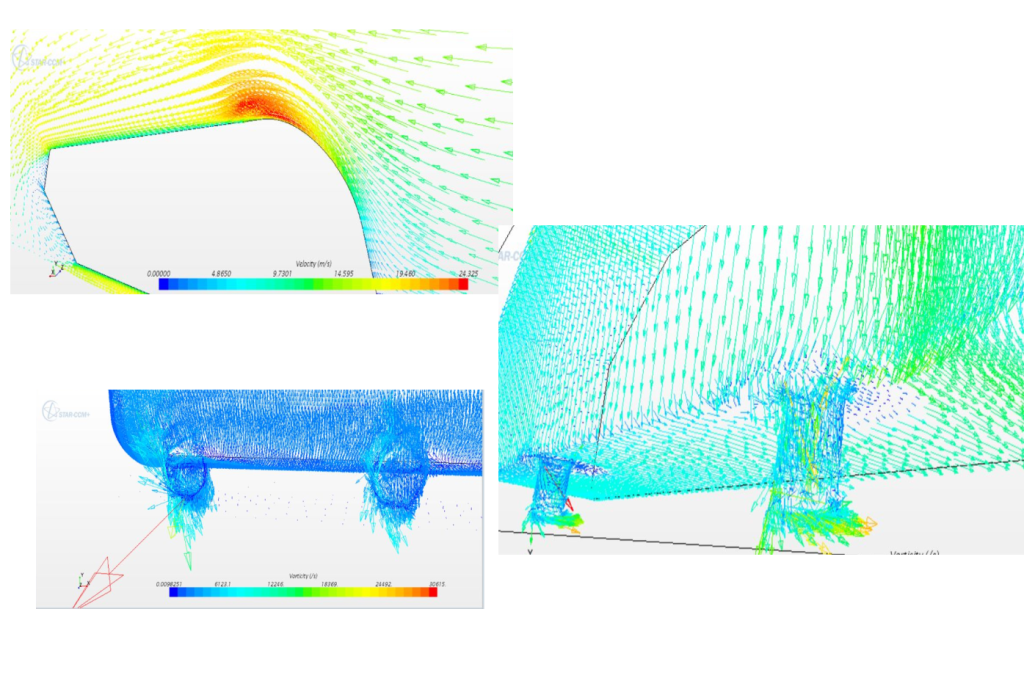
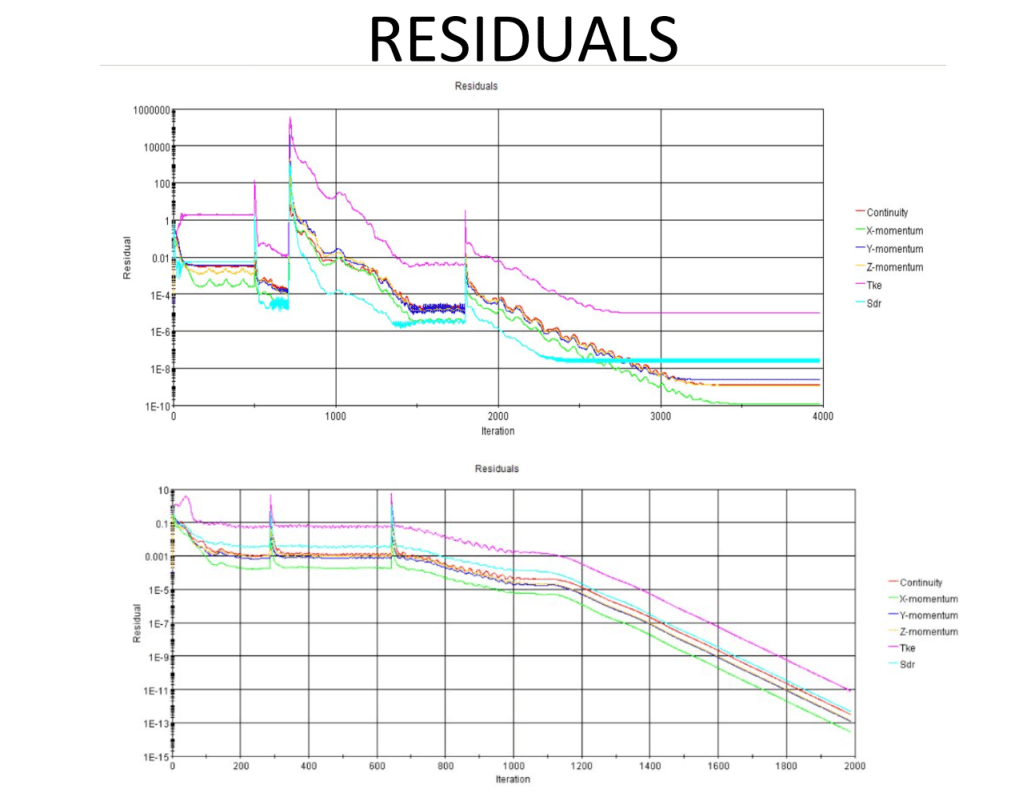
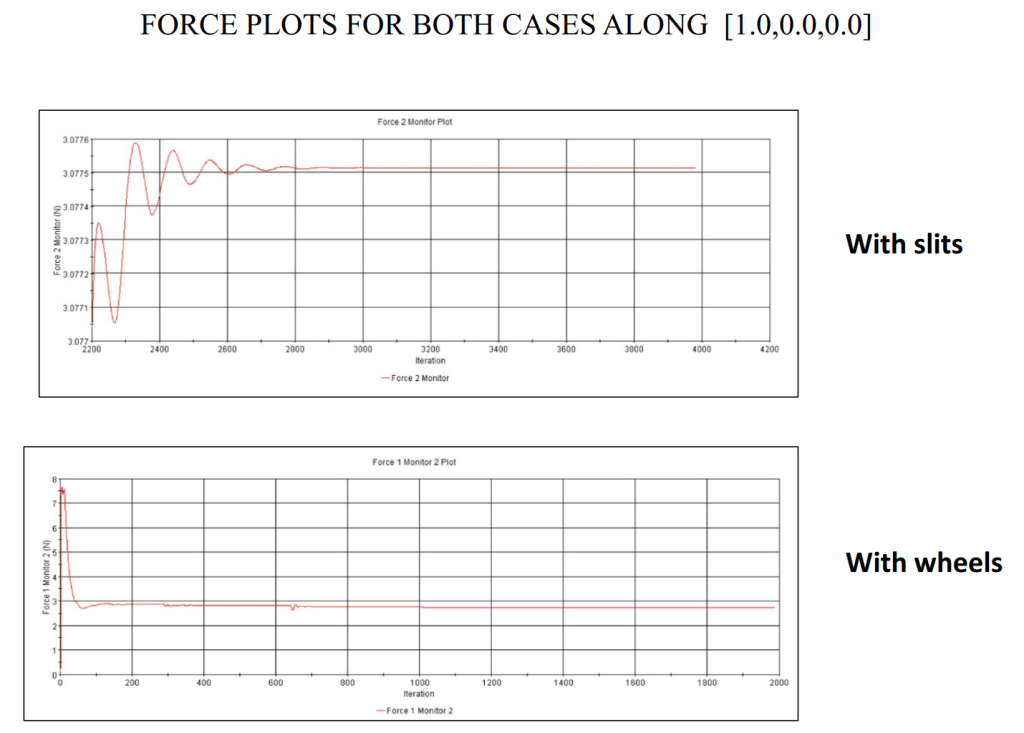
STAR CCM+ analysis of Ahmed body and comparison of fluid flow around wheel and slit design
Compared the reduction in drag and conducted computational fluid dynamic simulations between the two models to study the difference in aerodynamic characteristics between the two.
Found force plots for the design with wheels and the one We see that even though the Ahmed body is such a small scale experiment, the evaluation suggests that by removing the slits and adding a tyre (or in our case a wheel) can make all the difference in the values of the drag obtained.
Learned about the drag developed by looking at the velocity analysis.